User's Manual 414 Document #: LTRT-12809
Mediant 800 MSBR
example, a company has a PBX with extensions 555-1000 to 555-1999, and a caller dials
555-1234, the local central office (CO) would forward, for example, only 234 to the PBX.
The PBX would then ring extension 234.
DID wink enables the originating end to seize the line by going off-hook. It waits for
acknowledgement from the other end before sending digits. This serves as an integrity
check that identifies a malfunctioning trunk and allows the network to send a re-order tone
to the calling party.
The "start dial" signal is a wink from the PBX to the FXO device. The FXO then sends the
last four to five DTMF digits of the called number. The PBX uses these digits to complete
the routing directly to an internal station (telephone or equivalent)
DID Wink can be used for connection to EIA/TIA-464B DID Loop Start lines
Both FXO (detection) and FXS (generation) are supported
29.14.2 FXO Operations for Tel-to-IP Calls
The FXO device provides the following FXO operating modes for Tel-to-IP calls:
Automatic Dialing (see 'Automatic Dialing' on page 414)
Collecting Digits Mode (see 'Collecting Digits Mode' on page 415)
FXO Supplementary Services (see 'FXO Supplementary Services' on page 415)
• Hold/Transfer Toward the Tel side
• Hold/Transfer Toward the IP side
• Blind Transfer to the Tel side
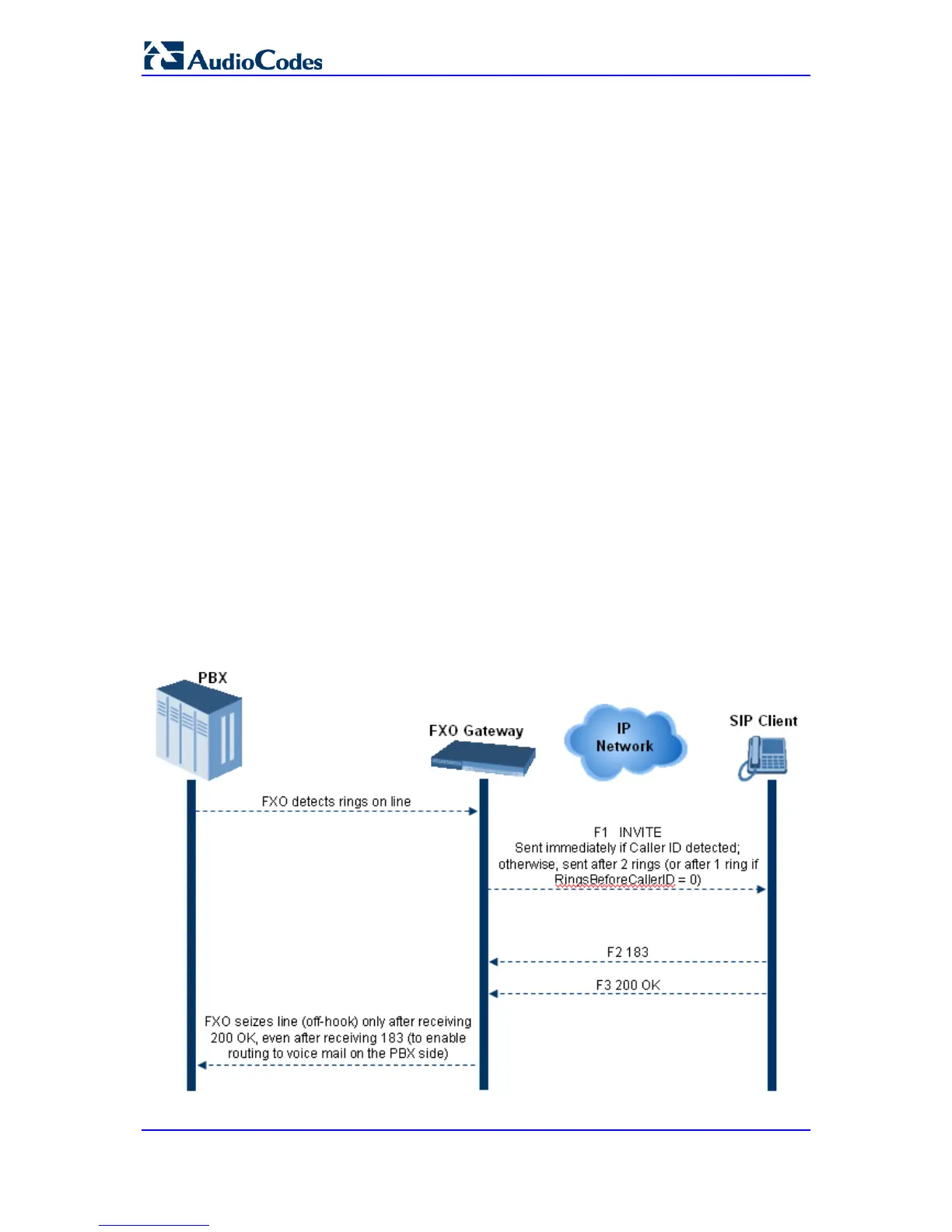
29.14.2.1 Automatic Dialing
Automatic dialing is defined using the Web interface's Automatic Dialing (TargetOfChannel
ini file parameter) page, described in see 'Configuring Automatic Dialing' on page 402.
The SIP call flow diagram below illustrates Automatic Dialing.

 Loading...
Loading...