Microstream CO2 monitoring
352 Instructions for use – Infinity Acute Care System – Monitoring Applications VG6.n
Troubleshooting
In addition to evaluating the clinical status of a
patient, CO2 waveforms can help troubleshoot
equipment problems. The following table shows
how CO
2 waveforms can be used to identify
common problems.
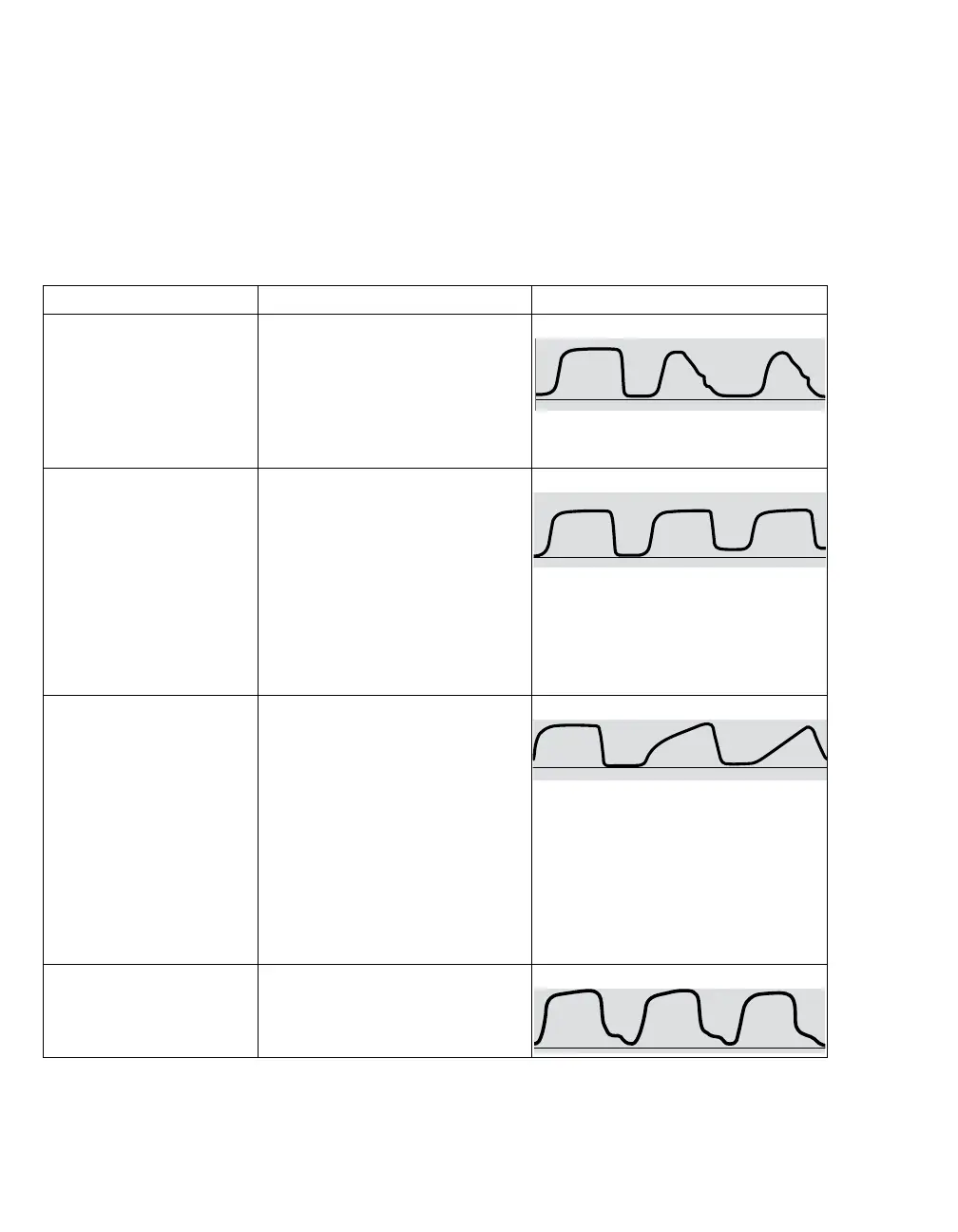
Description Cause CO
2 waveform
Alveolar plateau showing a
downward slope that
merges with a descending
limb.
– Inadequate seal around the
endotracheal tube
– Leaky or deflated endotracheal
or tracheostomy cuff
– Artificial airway that is too small
for the patient
Elevated waveform
baseline with
corresponding increase in
CO
2 level.
Rebreathing due to one of the
following causes:
– Insufficient expiratory time
– Faulty expiratory valve
– Inadequate inspiratory flow
– Malfunction of a CO
2 absorber
system
– Partial rebreathing circuits
Change in slope of
ascending limb. Possible
absence of an alveolar
plateau.
Obstruction caused by one of the
following:
– Partial obstruction in expiratory
hose of breathing circuit
– Foreign matter in upper airway
– Partially kinked or occluded
artificial airway
– Herniated endotracheal or
tracheostomy tube cuff
– Bronchospasm
Elevated baseline, with
pronounced slope on
descending limb
– Faulty ventilator circuit valve
– Rebreathing (see above)
 Loading...
Loading...