User's Manual 186 Document #: LTRT-89730
Mediant 3000
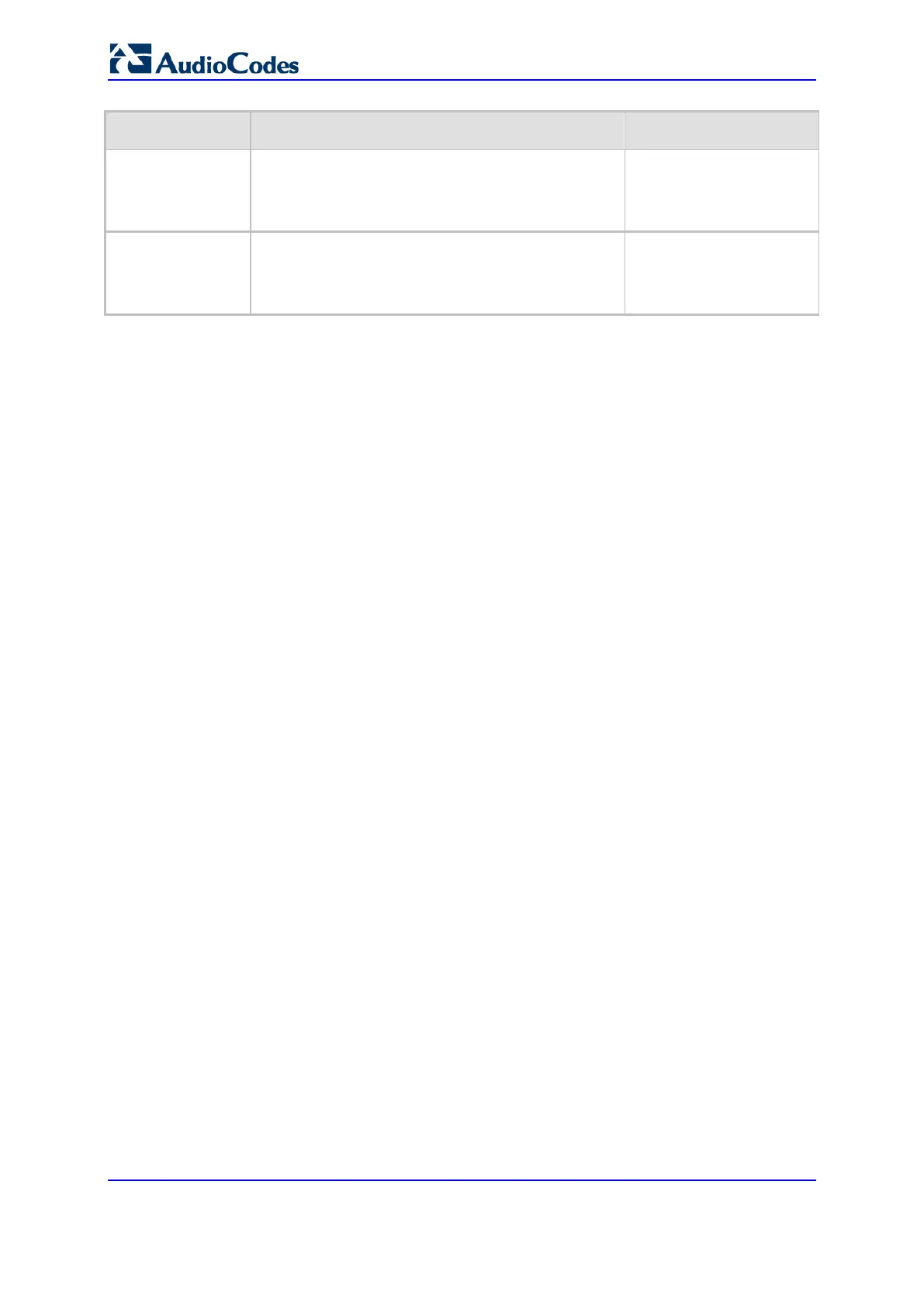
Type Description Syslog String
Failure
Other local rejects (prior to SIP 180 response)
Remote rejects (prior to SIP 180 response)
establish-local-reject
establish-remote-
reject
Abnormal Flow
Requests and responses without a matching
transaction user (except ACK requests)
Requests and responses without a matching
transaction (except ACK requests)
flow-no-match-tu
flow-no-match-
transaction
14.4 IPSec and Internet Key Exchange
IP security (IPSec) and Internet Key Exchange (IKE) protocols are part of the IETF
standards for establishing a secured IP connection between two applications (also referred
to as peers). Providing security services at the IP layer, IPSec and IKE are transparent to
IP applications. IPSec and IKE are used together to provide security for control and
management (e.g., SNMP and Web) protocols, but not for media (i.e., RTP, RTCP and
T.38).
IKE is used to obtain the Security Associations (SA) between peers (the device and the
application it’s trying to contact). The SA contains the encryption keys and profile used by
IPSec to encrypt the IP stream. IKE negotiation comprises the following two phases:
Main Mode (creates a secured channel for the Quick mode by obtaining a "master"
encryption key, without any prior keys, and authenticates the peers to each other):
• SA negotiation: The peers negotiate their capabilities using up to four proposals.
Each proposal includes the Encryption method, Authentication algorithm, and the
Diffie-Hellman (DH) group. The master key’s lifetime is also negotiated. For
configuring IPSec proposals, see ''Configuring IP Security Proposal Table'' on
page 187.
• Key exchange (DH): The DH protocol creates the master key. DH requires both
peers to agree on certain mathematical parameters, known as the "group".
• Authentication: The two peers authenticate one another using a pre-shared key
(configured in ''Configuring IP Security Associations Table'' on page 188) or by
using certificate-based authentication.
Quick Mode (creates the encrypted IPSec tunnel once initial security is set up):
• SA negotiation: An IPSec SA is created by negotiating encryption and
authentication capabilities using the same proposal mechanism as in Main mode.
• Key exchange: A symmetrical key is created for encrypting IPSec traffic; the
peers communicate with each other in encrypted form, secured by the previously
negotiated "master" key.
IKE specifications summary:
Authentication methods: pre-shared key or certificate-based authentication
Main mode supported for IKE Phase 1
DH group 1 or group 2
Encryption algorithms: Data Encryption Standard (DES), Advanced Encryption
Standard (AES), and 3DES
Hash algorithms: SHA1 and MD5
IPSec is responsible for securing the IP traffic. This is accomplished by using the
Encapsulation Security Payload (ESP) protocol to encrypt (and decrypt) the IP payload.
This is configured in the IPSec Security Association table (see ''Configuring IP Security

 Loading...
Loading...











