Zynq-7000 AP SoC and 7 Series FPGAs MIS v4.1 152
UG586 November 30, 2016
www.xilinx.com
Chapter 1: DDR3 and DDR2 SDRAM Memory Interface Solution
During the centering substage the write DQS is centered in the write DQ window based on
the edges found during the edge detection stage. At the end of this stage, write DQS should
be centered in the write DQ window. DQS to CK are not correct therefore write leveling is
performed at the end of this stage of calibration.
With every stage 3 tap decrease, the stage 2 taps are increased by 2 to maintain the DQS to
CK relationship established during write leveling. Similarly, with every stage 3 tap
increment, the stage 2 taps are decreased by 2. If stage 2 taps reach 0 or 63, stage 3 tap
increment/decrement is allowed to proceed up to the left and right limit values to avoid
t
DQSS
violation. At the end of this stage of calibration, write leveling is redone to align DQS
and CK using stage 2 taps.
Write Calibration
Write calibration is performed after both stages of read leveling because correct data
pattern sequence detection is necessary for this stage of calibration. Write calibration is
required to align DQS to the correct CK edge. During write leveling, DQS is aligned to the
nearest rising edge of CK. However, this might not be the edge that captures the write
command. Depending on the interface type (UDIMM, RDIMM, or component), the DQS
could either be one CK cycle earlier than, one CK cycle later than, or aligned to the CK edge
that captures the write command. Figure 1-67 shows several different scenarios based on
the initial phase relationship between DQS and CK for a UDIMM or RDIMM interface.
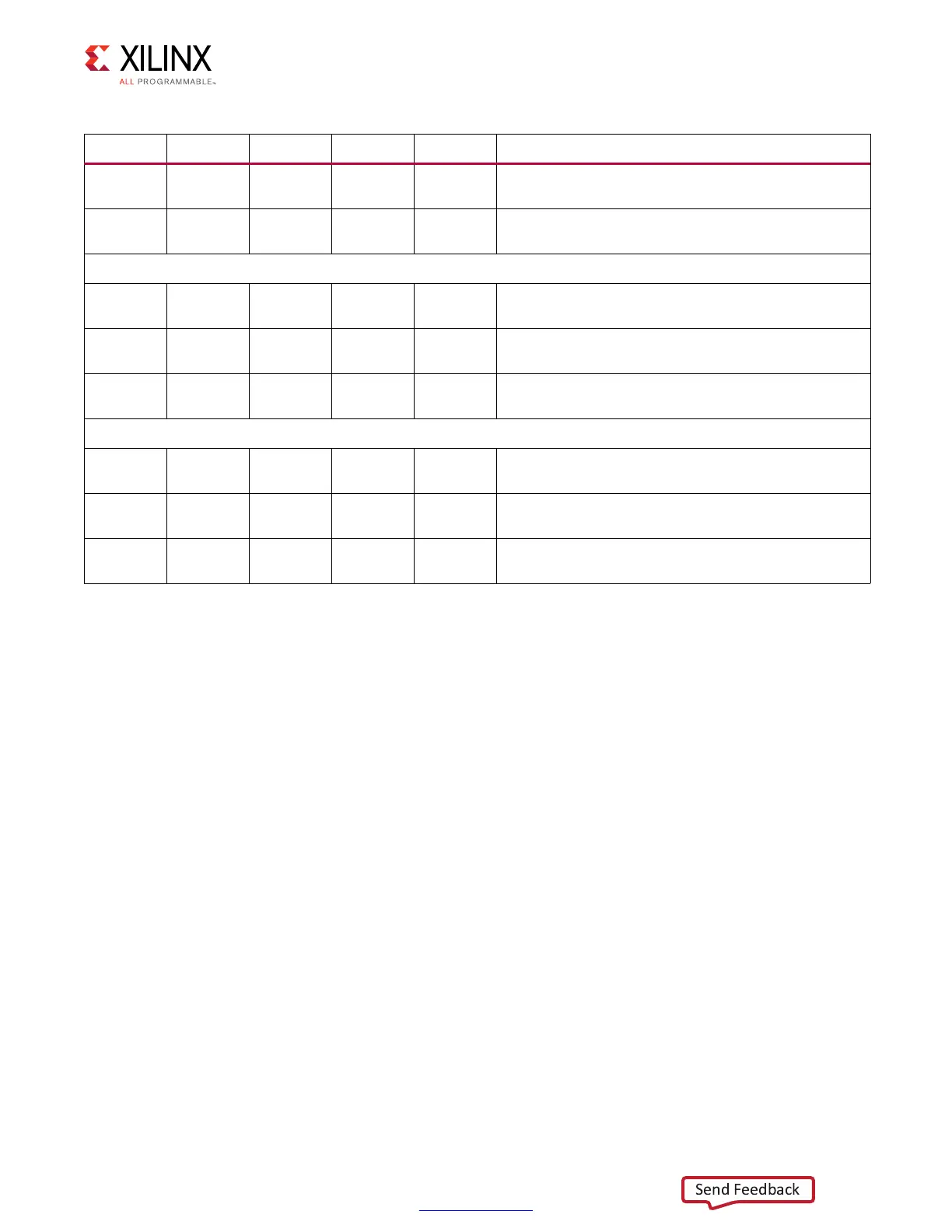
Case 3 Found
Not
Found
Not
Found
Not
Found
(fuzz2zero + lim2ocal_stg3_right_lim)/2
Case 4
Not
Found
Found
Not
Found
Not
Found
(lim2ocal_stg3_left_lim + zero2fuzz)/2
Noise/Jitter Region
Case 1 Found Found Found
Not
Found
(fuzz2zero + zero2fuzz)/2
Case 2
Not
Found
Found Found Found (zero2fuzz + fuzz2oneeighty)/2 – 90
o
Case 3
Not
Found
Found Found
Not
Found
(zero2fuzz + fuzz2oneeighty)/2 – 90
o
Fall Window 180
o
to 225
o
Case 1
Not
Found
Found Found Found (zero2fuzz + fuzz2oneeighty)/2 – 90
o
Case 2
Not
Found
Not
Found
Found Found (fuzz2oneeighty + oneeighty2fuzz)/2 – 180
o
Case 3
Not
Found
Not
Found
Found
Not
Found
(fuzz2oneeighty + lim2ocal_stg3_right_lim)/2 – 180
o
Table 1-60: Starting Scenarios for Write DQS (Cont’d)
Start DQS f2z z2f f2o o2f Center Equation

 Loading...
Loading...