Version 5.2 349 September 2007
SIP User's Manual 7. Telephony Capabilities
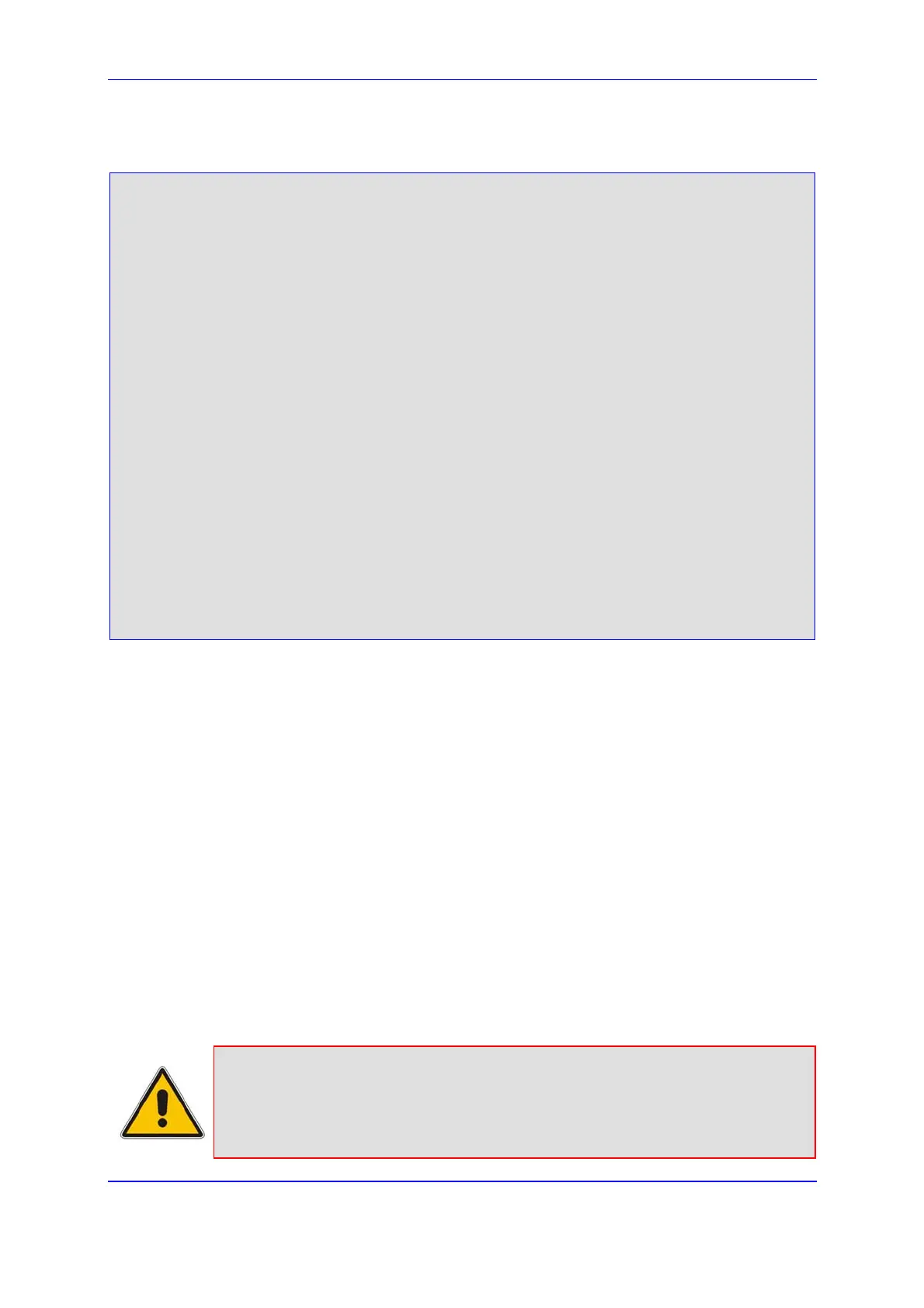
Below is an example of SIP messages implementing the X-Detect header:
INVITE sip:101@10.33.2.53;user=phone SIP/2.0
Via: SIP/2.0/UDP 10.33.2.53;branch=z9hG4bKac5906
Max-Forwards: 70
From: "anonymous" <sip:anonymous@anonymous.invalid>;tag=1c25298
To: <sip:101@10.33.2.53;user=phone>
Call-ID: 11923@10.33.2.53
CSeq: 1 INVITE
Contact: <sip:100@10.33.2.53>
X- Detect: Request=CPT,FAX
SIP/2.0 200 OK
Via: SIP/2.0/UDP 10.33.2.53;branch=z9hG4bKac5906
From: "anonymous" <sip:anonymous@anonymous.invalid>;tag=1c25298
To: <sip:101@10.33.2.53;user=phone>;tag=1c19282
Call-ID: 11923@10.33.2.53
CSeq: 1 INVITE
Contact: <sip:101@10.33.2.53>
X- Detect: Response=CPT,FAX
INFO sip:101@10.33.2.53;user=phone SIP/2.0
Via: SIP/2.0/UDP 10.33.2.53;branch=z9hG4bKac5906
Max-Forwards: 70
From: "anonymous" <sip:anonymous@anonymous.invalid>;tag=1c25298
To: <sip:101@10.33.2.53;user=phone>
Call-ID: 11923@10.33.2.53
CSeq: 1 INVITE
Contact: <sip:100@10.33.2.53>
X- Detect: Response=CPT,FAX
Content-Type: Application/X-Detect
Content-Length: xxx
Type = CPT
Subtype = SIT
7.4 RTP Multiplexing (ThroughPacket)
The gateway supports a proprietary method to aggregate RTP streams from several
channels to reduce the bandwidth overhead caused by the attached Ethernet, IP, UDP,
and RTP headers, and to reduce the packet / data transmission rate. This option reduces
the load on network routers and can typically save 50% (e.g., for G.723) on IP bandwidth.
RTP Multiplexing (ThroughPacket™) is accomplished by aggregating payloads from
several channels that are sent to the same destination IP address into a single IP packet.
RTP multiplexing can be applied to the entire gateway (refer to 'Configuring the RTP /
RTCP Settings' on page 172) or to specific IP destinations using the IP Profile feature
(refer to 'IP Profile Settings' on page 136).
To enable RTP Multiplexing, set the parameter RemoteBaseUDPPort to a nonzero value.
Note that the value of RemoteBaseUDPPort on the local gateway must equal the value of
BaseUDPPort of the remote gateway. The gateway uses these parameters to identify and
distribute the payloads from the received multiplexed IP packet to the relevant channels.
In RTP Multiplexing mode, the gateway uses a single UDP port for all incoming multiplexed
packets and a different port for outgoing packets. These ports are configured using the
parameters L1L1ComplexTxUDPPort and L1L1ComplexRxUDPPort. When RTP
Multiplexing is used, call statistics aren’t available (since there is no RTCP flow).
Notes:
• RTP Multiplexing must be enabled on both gateways.
• When VLANs are imlemented, the RTP Multiplexing mechanism is not
supported.
 Loading...
Loading...