SIP User's Manual 366 Document #: LTRT-68806
Mediant 2000 & TP-1610 & TP-260/UNI
After start-up is complete and the operational software is running, the gateway continues to
use the Ethernet port used for program load. The gateway switches over from one Ethernet
port to the other every time an Ethernet link carrier loss is detected on the active Ethernet
port, and if the Ethernet link of the other port is operational. Switchover takes place only
once per link loss (that is, the ‘secondary’ interface stays the active one even if the
‘primary’ interface has returned to life). After start-up, the gateway generates a gratuitous
ARP message each time a switchover occurs.
For correct functionality of the redundancy mechanism, it's recommended to configure both
links to the same mode. It is essential that both link partners (the primary link partner and
the secondary link partner) have the same capabilities. This ensures that whenever a
switchover occurs, the gateway is able to provide at least the same Ethernet services as
were provided prior to the switchover. In addition, it's recommended to set the physical
secondary link prior to the gateway being reset (since the MAC configuration cannot be
changed thereafter).
Note that since the two Ethernet ports use the same MAC address, the external switches
connected to the gateways can in some cases create a noticeable switchover delay due to
their internal switching logic, though on the gateway level, the switchover delay is minimal
(milliseconds).
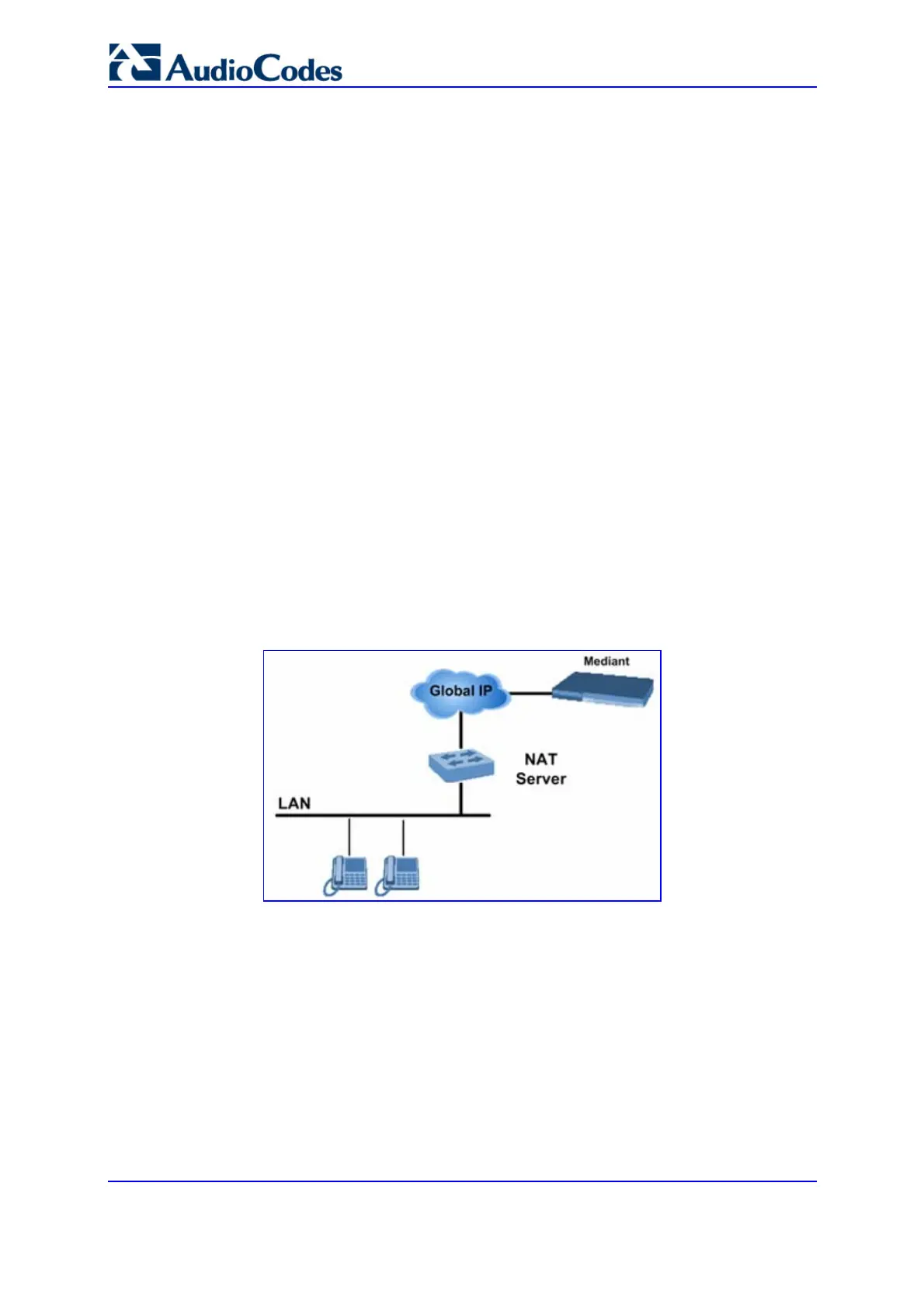
8.3 NAT (Network Address Translation) Support
Network Address Translation (NAT) is a mechanism that maps a set of internal IP
addresses used within a private network to global IP addresses, providing transparent
routing to end hosts. The primary advantages of NAT include (1) Reduction in the number
of global IP addresses required in a private network (global IP addresses are only used to
connect to the Internet); (2) Better network security by hiding its internal architecture.
The following figure illustrates the gateway's supported NAT architecture.
The design of SIP creates a problem for VoIP traffic to pass through NAT. SIP uses IP
addresses and port numbers in its message body and the NAT server can’t modify SIP
messages and therefore, can’t change local to global addresses.
Two different streams traverse through NAT: signaling and media. A gateway (located
behind a NAT) that initiates a signaling path has problems in receiving incoming signaling
responses (they are blocked by the NAT server). Furthermore, the initiating gateway must
notify the receiving gateway where to send the media.

 Loading...
Loading...