P44x/EN AP/Hb
MiCOM P40 Agile P442, P444
(AP) 5-
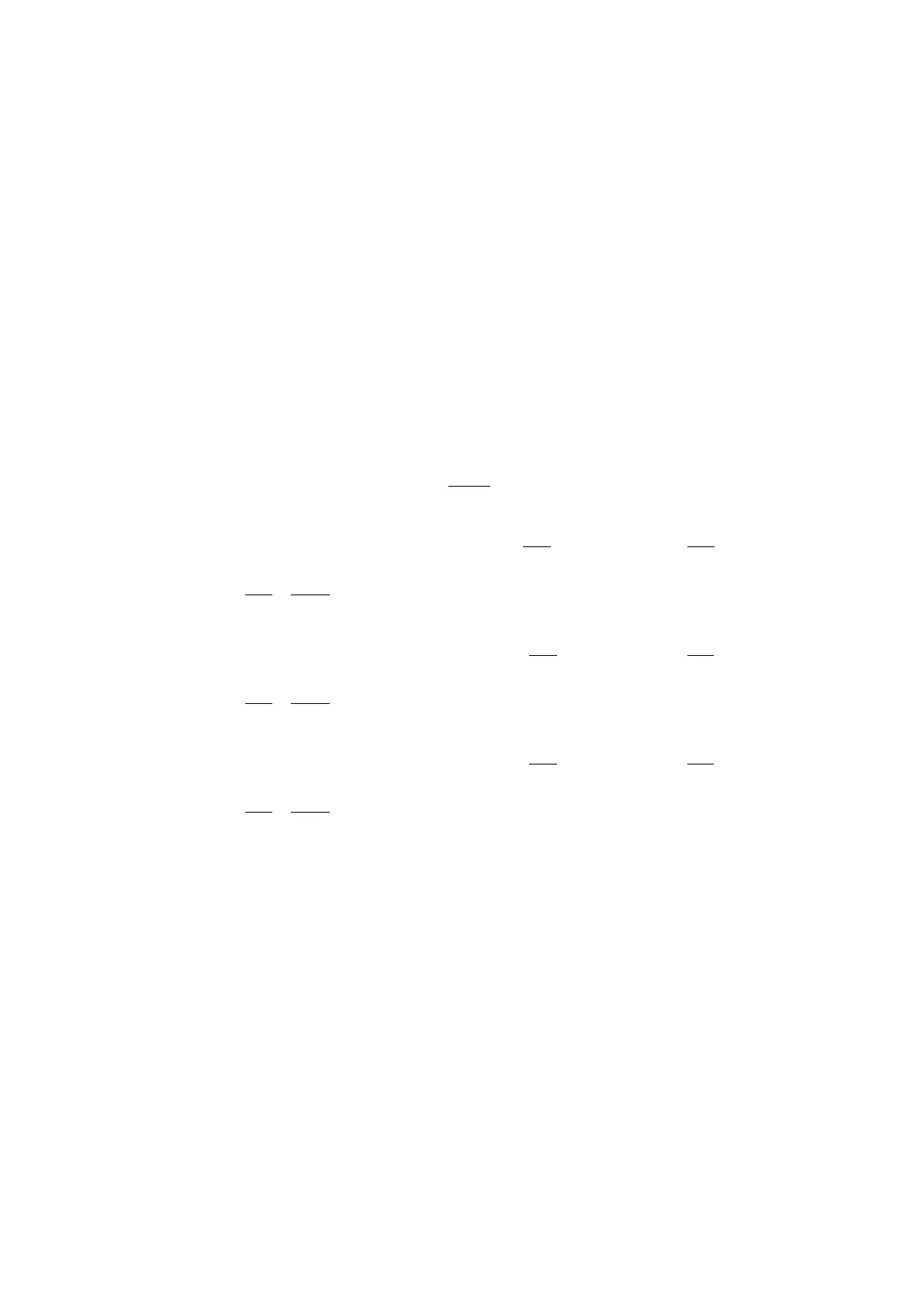
The impedance model for the phase-to-phase loop is:
V
αβ = ZL x Dfault x Iαβ + Rfault /2 x Ifault
with
αβ = phase AB, BC or CA
The model for the current Ifault circulating in the fault I
αβ.
V
AB
= 2Z
1
.D
fault
.I
AB
+ R
fault
.I
fault
V
BC
= 2Z
1
.D
fault
.I
BC
+ R
fault
.I
fault
V
CA
= 2Z
1
.D
fault
.I
CA
+ R
fault
.I
fault
= 3 phase-to-phase loops are continuously monitored and computed for each sample.
V
αβ
= 2Z
1
.D
fault
.I
αβ
+ R
fault
.I
fault
V
αβ
= 2(R
1
+ j. X
1
).D
fault
.I
αβ
+ R
fault
.I
fault
V
αβ
= 2R
1
.D
fault
.I
αβ
+ 2j. X
1
.D
fault
.I
αβ
+ R
fault
.I
fault
V
αβ
= 2R
1
.D
fault
.I
αβ
+ 2X
1
.D
fault
.
+ R
fault
.I
fault
V
AB
= R
1
.D
fault
.(I
A
– I
B
) + (L
AA
–L
AB
).D
fault
.
+ (L
AB
–L
BB
).D
fault
.
+ (L
AC
–L
BC
).D
fault
.
+
.I
fault
V
BC
= R
1
.D
fault
.(I
B
– I
C
) + (L
AB
–L
AC
).D
fault
.
+ (L
BB
–L
BC
).D
fault
.
+ (L
BC
–L
CC
).D
fault
.
+
.I
fault
V
CA
= R
1
.D
fault
.(I
C
– I
A
) + (L
AC
–L
AA
).D
fault
.
+ (L
BC
–L
AB
).D
fault
.
+ (L
CC
–L
AC
).D
fault
.
+
.I
fault
Impedance measurement algorithms work with instantaneous values (current and voltage).
The derived current value (dI/dt) is obtained by using a FIR filter.
2.2 "Delta" Algorithm
The patented high-speed algorithm has been proven with at least 20 years of service at all
voltage levels from MV to EHV networks. The P44x relay has ultimate reliability of phase
selection and directional decision far superior to standard distance techniques using
superimposed algorithms. These algorithms or delta algorithms are based on transient
components and they are used for the following functions which are computed in parallel:
Detection of the fault
By comparing the superimposed values to a threshold which is low enough to be crossed
when a fault occurs and high enough not to be crossed during normal switching outside of
the protected zones.
Establishing the fault direction
Only a fault can generate superimposed values; therefore, it is possible to determine
direction by measuring the transit direction of the superimposed energy.

 Loading...
Loading...