44x/EN AP/Hb6
-50 MiCOM P40 Agile
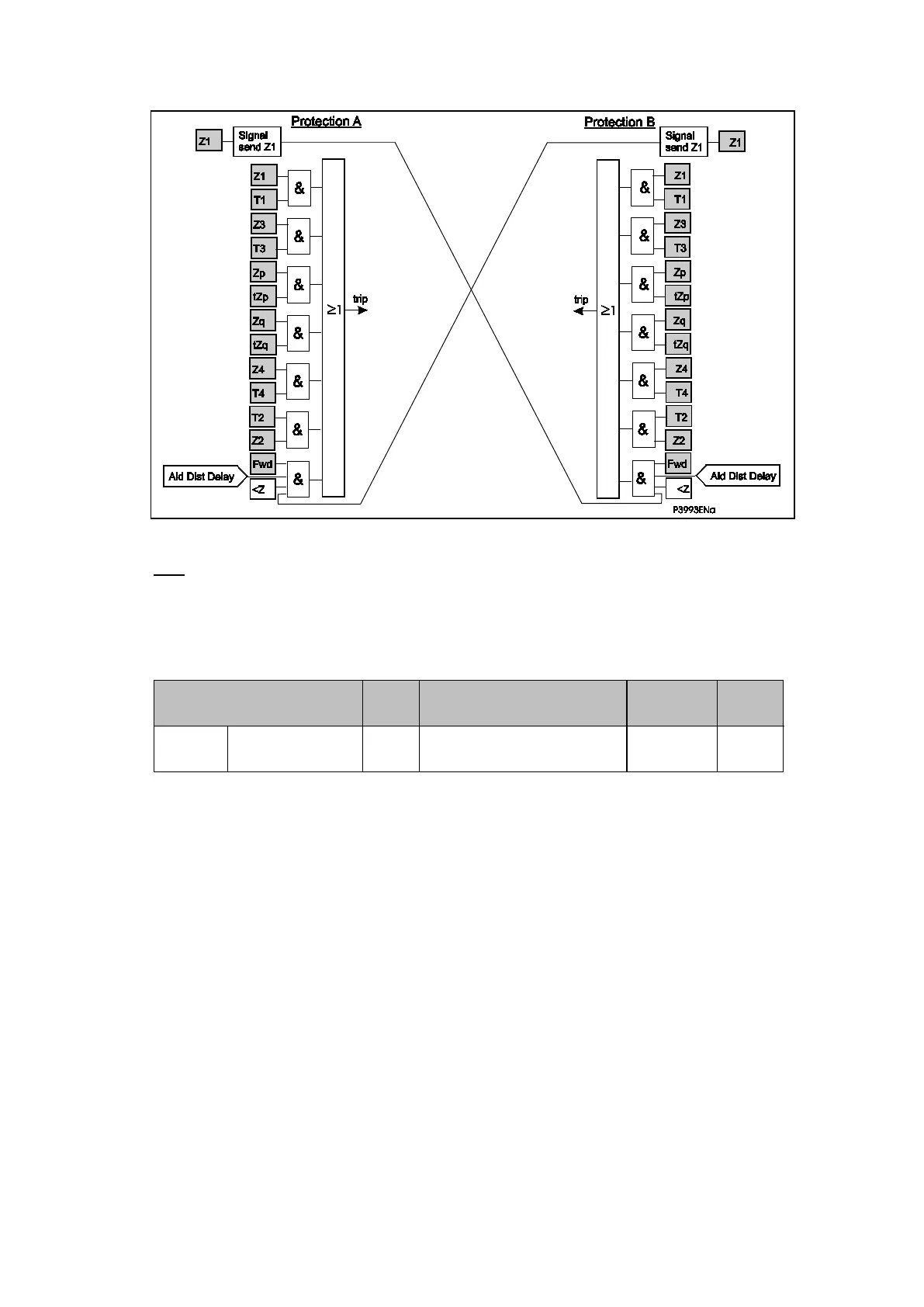
Figure 26: PUP fwd permissive underreach scheme
Key:
Fwd = Forward fault detection (DDB: ‘Dist Fwd’ or ‘DEF Fwd’);
<Z = Underimpedance Started: Z2 or Z3.
Trip logic:
IEC Standard
Send
Trip Logic Application
User
setting
448.15.11 PUP or PUTT Z1
Fwd.CR.’Aid Dist Delay’ + Z1.T1 +
Z2.T2 +...
Z1 = 80% ZL PUP Fwd
3.2.1.3 Permissive Overreach Transfer Trip Schemes POP Z2 and POP Z1
The P442 and P444 relays offer two variants of permissive overreach protection schemes
(POP), having the following common features/requirements:
• The scheme requires a duplex signalling channel to prevent possible relay
maloperation due to spurious keying of the signalling equipment. This is necessary
because the signalling channel is keyed for faults external to the protected line.
• The POP Z2 scheme may be more advantageous than permissive underreach
schemes for the protection of short transmission lines, since the resistive coverage of
the Zone 2 elements may be greater than that of the Zone 1 elements.
• Current reversal guard logic is used to prevent healthy line protection maloperation for
the high speed current reversals experienced in double circuit lines, caused by
sequential opening of circuit breakers.
• If the signalling channel fails, Basic distance scheme tripping will be available.
3.2.1.3.1 Permissive Overreach Protection with Overreaching Zone 2 (POP Z2)
Figure 27 shows the zone reaches, and Figure 28 the simplified scheme logic. The signalling
channel is keyed from operation of the overreaching zone 2 elements of the relay. If the
remote relay has picked up in zone 2, then it will operate with no additional delay upon
receipt of this signal. The POP Z2 scheme also uses the reverse looking zone 4 of the relay
as a reverse fault detector. This is used in the current reversal logic and in the optional weak
infeed echo feature.

 Loading...
Loading...