P44x/EN AP/Hb
MiCOM P40 Agile P442, P444
(AP) 5-
Trip logic:
IEC Standard
Carrier
Trip Logic Application
User
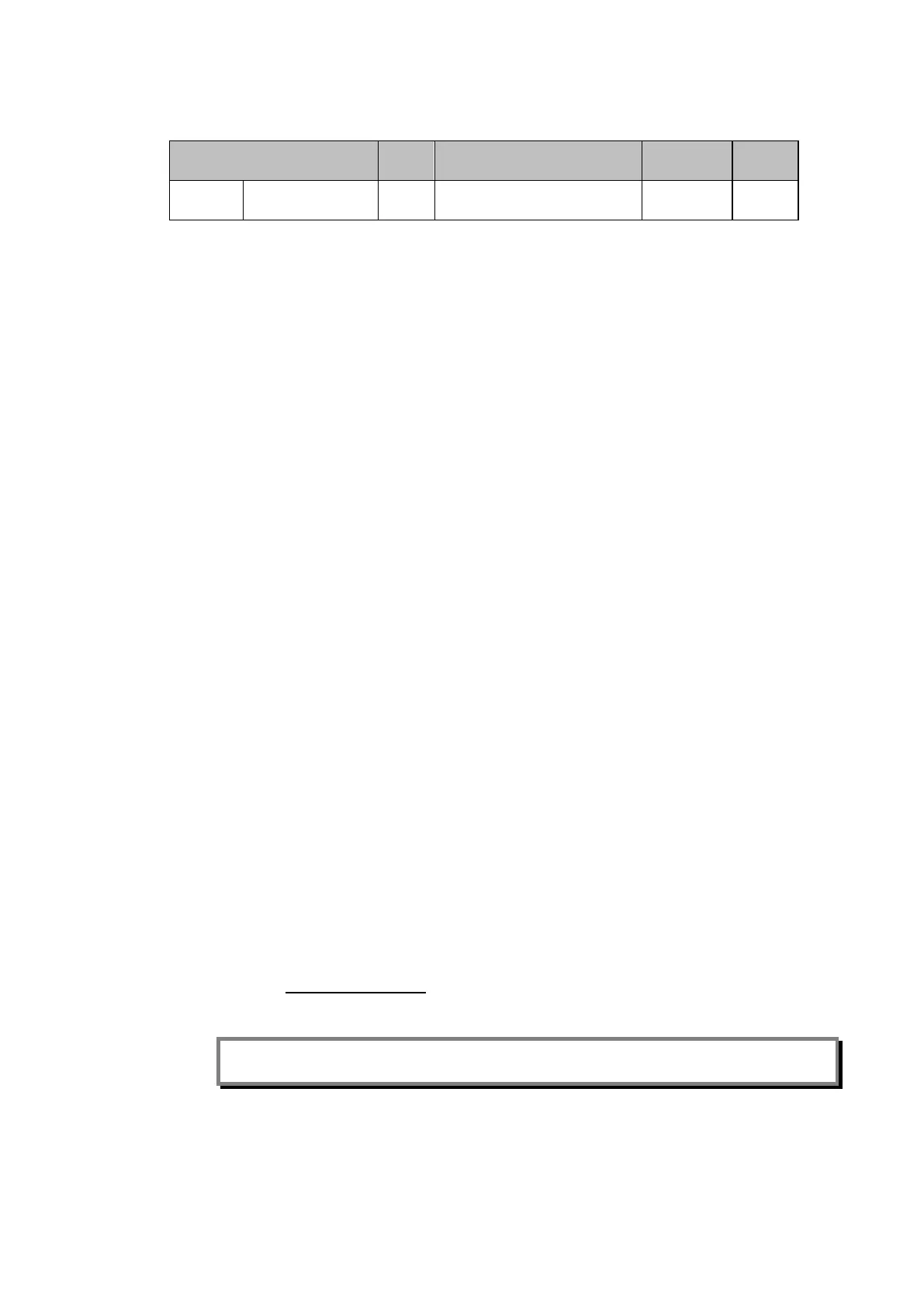
448.15.16 POR1 or POP or POTT Z1
Z1.CR.’Aid Dist Delay’ + Z1.T2 + Z2.T2
+ Z3.T3...
Z1 > ZL POP Z1
3.2.1.4 Blocking Schemes BOP Z2 and BOP Z1
The P442 and P444 relays offer two variants of blocking overreach protection schemes
(BOP). With a blocking scheme, the signalling channel is keyed from the reverse looking
zone 4 element, which is used to block fast tripping at the remote line end. Features are as
follows:
• BOP schemes require only a simplex signalling channel.
• Reverse looking Zone 4 is used to send a blocking signal to the remote end to prevent
unwanted tripping.
• When a simplex channel is used, a BOP scheme can easily be applied to a multi-
terminal line provided that outfeed does not occur for any internal faults.
• The blocking signal is transmitted over a healthy line, and so there are no problems
associated with power line carrier signalling equipment.
• BOP schemes provide similar resistive coverage to the permissive overreach
schemes.
• Fast tripping will occur at a strong source line end, for faults along the protected line
section, even if there is weak or zero infeed at the other end of the protected line.
• If a line terminal is open, fast tripping will still occur for faults along the whole of the
protected line length.
• If the signalling channel fails to send a blocking signal during a fault, fast tripping will
occur for faults along the whole of the protected line, but also for some faults within
the next line section.
• If the signalling channel is taken out of service, the relay will operate in the
conventional Basic mode.
• A current reversal guard timer is included in the signal send logic to prevent unwanted
trips of the relay on the healthy circuit, during current reversal situations on a parallel
circuit.
• To allow time for a blocking signal to arrive, a short time delay on aided tripping, Aided
distribution
transmission delay time
, must be used, as follows:
Recommended ‘Aid Dist Delay’ setting: Max. signalling channel operating time + 14ms
3.2.1.4.1 Blocking Overreach Protection with Overreaching Zone 1 (BOP Z1)
This scheme is similar to that used in the Alstom Grid EPAC and PXLN relays. Figure 31
shows the zone reaches, and Figure 32 the simplified scheme logic. The signalling channel
is keyed from operation of the reverse zone 4 elements of the relay. If the remote relay has
picked up in overreaching zone 1, then it will operate after the Transmission Time (‘Distance
schemes / Aid Dist Delay’) time-delay if no block is received.
Note: The fastest tripping is always subject to the aided distance time-delay (‘Aid Dist
Delay’).
Send logic: Reverse Zone 4
Trip logic: Zone 1, plus Channel NOT Received, delayed by ‘Aid Dist Delay’.

 Loading...
Loading...