44x/EN AP/Hb6
-110 MiCOM P40 Agile
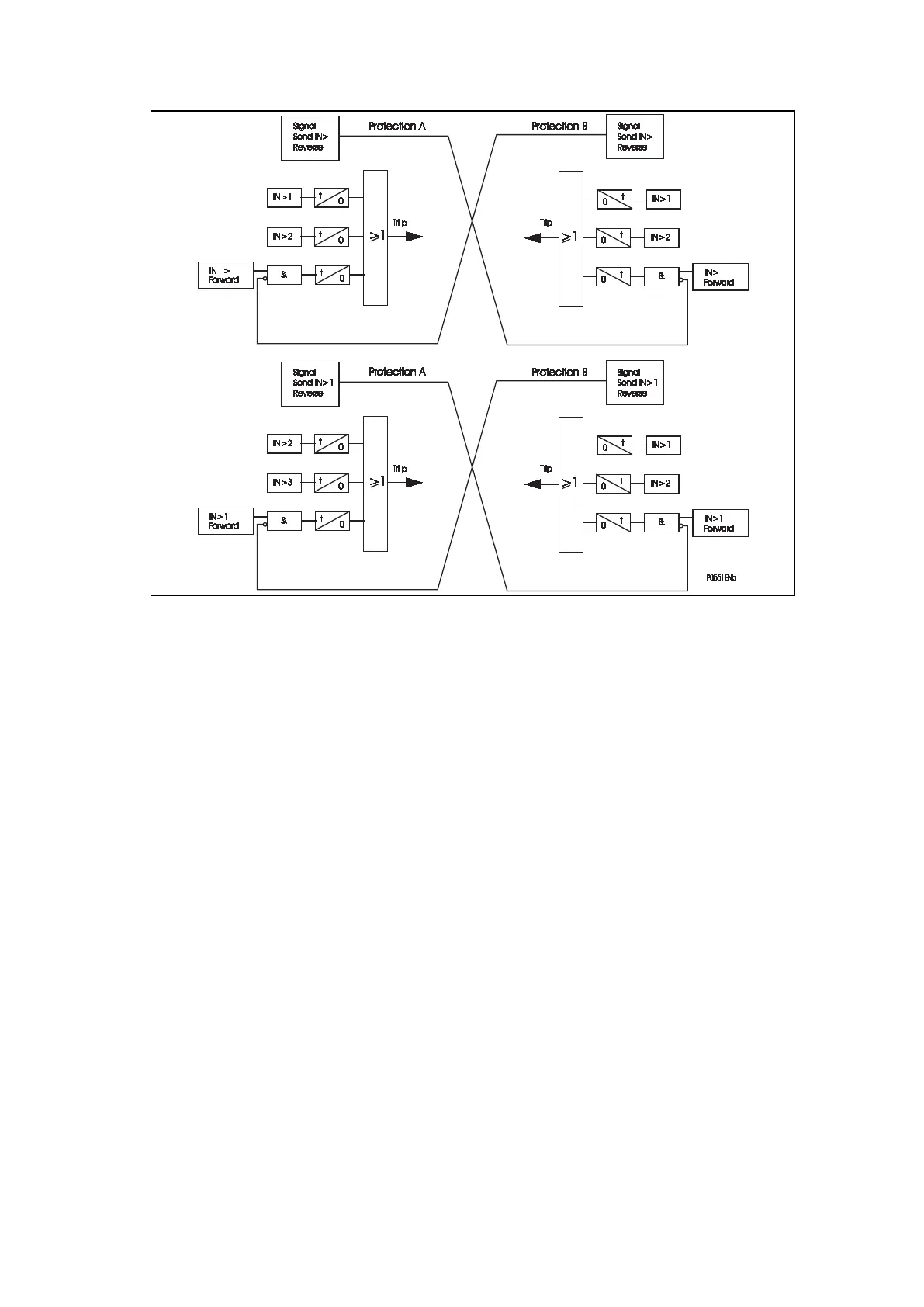
Figure 86: Logic diagram for the DEF blocking scheme
The scheme has the same features/requirements as the corresponding distance scheme
and provides sensitive protection for high resistance earth faults.
Where “t” is shown in the diagram this signifies the time delay associated with an element.
To allow time for a blocking signal to arrive, a short time delay on aided tripping must be
used. The recommended Time Delay setting = max. signalling channel operating time +
14 ms.
4.9 Thermal overload
Thermal overload protection can be used to prevent electrical plant from operating at
temperatures in excess of the designed maximum withstand. Prolonged overloading causes
excessive heating, which may result in premature ageing of the insulation, or in extreme
cases, insulation failure.
The relay incorporates a current based thermal replica, using load current to model heating
and cooling of the protected plant. The element can be set with both alarm and trip stages.
The heat generated within an item of plant, such as a cable or a transformer, is the resistive
loss (Ι
2
R × t). Therefore, heating is directly proportional to current squared. The thermal time
characteristic used in the relay is therefore based on current squared, integrated over time.
The relay automatically uses the largest phase current for input to the thermal model.
Equipment is designed to operate continuously at a temperature corresponding to its full load
rating, where heat generated is balanced with heat dissipated by radiation etc. Over
temperature conditions therefore occur when currents in excess of rating are allowed to flow
for a period of time.
The thermal protection also provides an indication of the thermal state in the measurement
column of the relay. The thermal state canbe reset by either an opto input (if assigned to this
function using the programmable scheme logic) or the relay menu, for example to reset after
injection testing. The reset function in the menu is found in the measurement column with the
thermal state.

 Loading...
Loading...