3 Communication with the controller
3.6 Ethernet over EtherCAT (EoE)
35
Lenze · i700 servo inverter · reference manual · DMS 3.0 EN · 06/2016 · TD06
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
3.6.4.1 Structure of the EtherCAT data telegram
The GCI protocol is used for communication.
The EtherCAT data telegram is shown below. Here, the GCI header represents the part of the
program that is independent of the type of command transmitted.
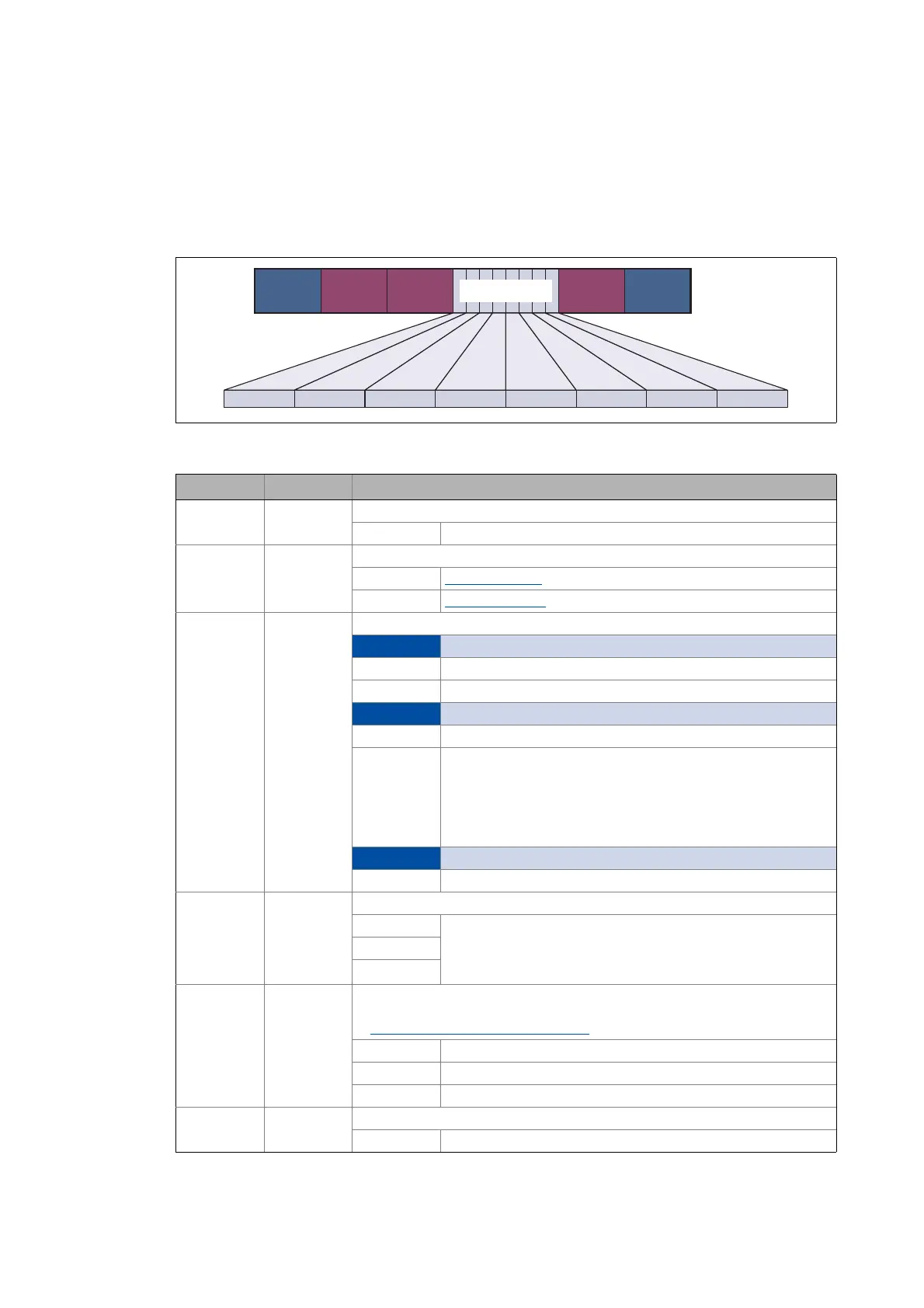
[3-2] Structure of the GCI header within the EtherCAT frame
EtherCAT
Header
IP Header
TCP/IP
Header
GCI Header
P0 ... P4
EtherCAT
Footer
GMQGMT GSV GTI SIZE SIZE res res
Field Size Description
GMT 1 byte GCI message type
0x01 Reserved
GSV 1 byte GCI service identification
0x82 Read parameters
0x83 Write parameters
GMQ 1 byte GCI message qualifier
Bit 7 rsp (Request/Response)
0Request
1Response
Bit 6 a (Abort)
0 Data transfer OK
1 Abort of the data transfer
• The transfer is either aborted by the client or the server of a
parameter data telegram.
• A message is aborted without any confirmation. If the client waits
for its message to be confirmed, it will receive the abort notice
instead.
Bit 5 ... bit 0 res (reserved)
0b000000 Data contents = 0
GTI 1 byte GCI transaction ID
0x00 Serial number (transaction identification)
• For each client a definite serial number (0 ... 255) is allocated.
• The serial number in the multitasking environment is used for
referencing to the calling tasks (reverse transaction).
...
0xFF
SIZE 2 bytes Length of the user data
• The user data area or the data telegram contains the parameter data.
Assignment of user data areas P0 ... P4
0x14 20 bytes
... ...
0x114 276 bytes
res 2 bytes Reserved
0x0000 Data contents = 0
 Loading...
Loading...