Engine Mechanical: 1D-3
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
Engine Mechanical Symptom Diagnosis
B718H11404002
Refer to “Engine Symptom Diagnosis in Section 1A
(Page 1A-7)”.
Compression Pressure Check
B718H11404001
The compression pressure reading of a cylinder is a
good indicator of its internal condition.
The decision to overhaul the cylinder is often based on
the results of a compression test. Periodic maintenance
records kept at your dealership should include
compression readings for each maintenance service.
NOTE
• Before checking the engine for
compression pressure, make sure that the
cylinder head nuts are tightened to the
specified torque values and the valves are
properly adjusted.
• Make sure that the battery is in fully-
charged condition.
1) Warm up the engine.
2) Remove the fuel tank. Refer to “Fuel Tank Removal
and Installation in Section 1G (Page 1G-9)”.
3) Remove the frame head covers, left and right.
(GSF1250/A) Refer to “Exterior Parts Removal and
Installation in Section 9D (Page 9D-6)”.
4) Remove all the spark plugs. Refer to “Ignition Coil /
Plug Cap and Spark Plug Removal and Installation in
Section 1H (Page 1H-4)”.
5) Install the compression gauge and adaptor in the
spark plug hole. Make sure that the connection is
tight.
Special tool
(A): 09915–64512 (Compression gauge)
(B): 09915–63311 (Compression gauge
attachment)
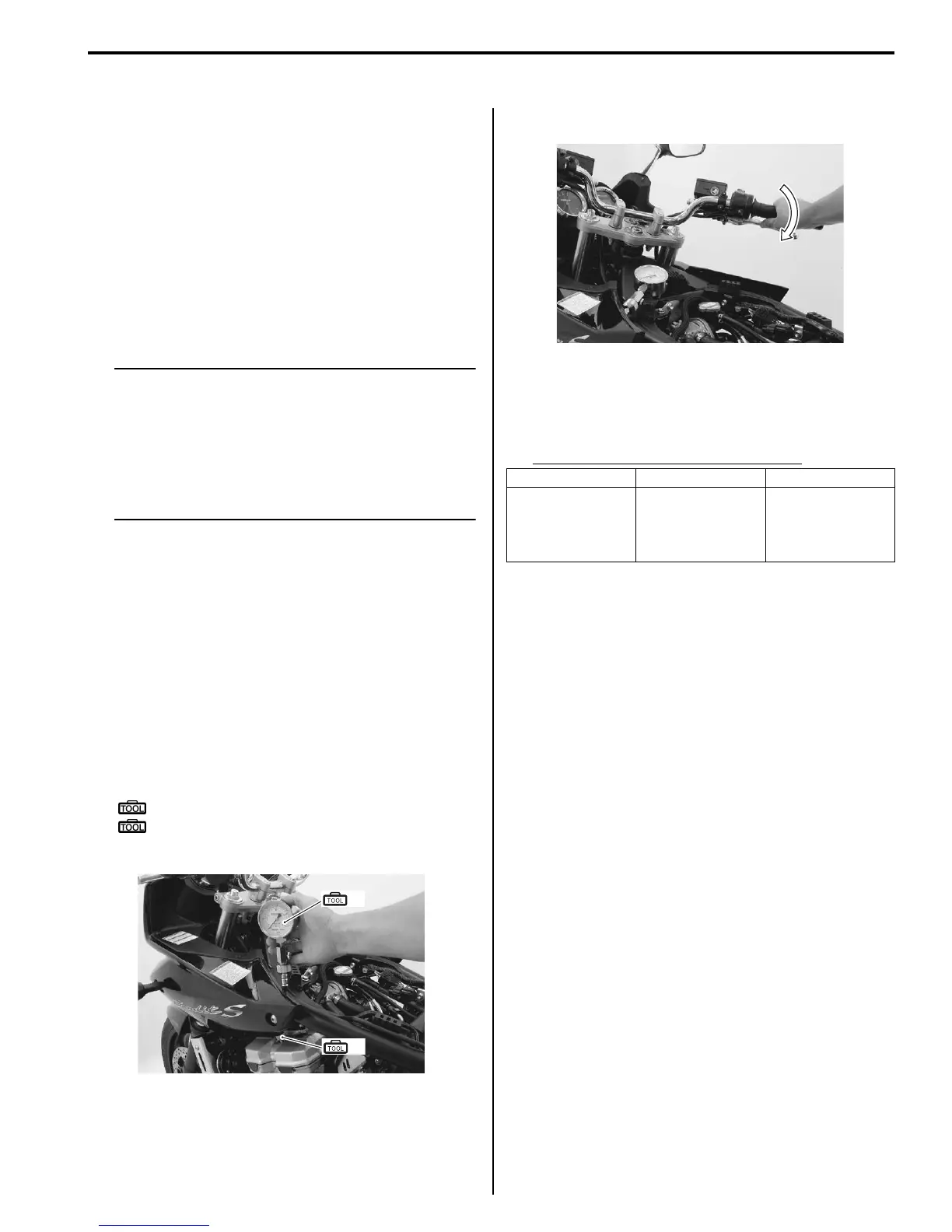
6) Keep the throttle grip in the fully-opened position.
7) Press the starter button and crank the engine for a
few seconds. Record the maximum gauge reading
as the cylinder compression.
8) Repeat this procedure with the other cylinders.
Compression pressure specification
Low compression pressure can indicate any of
the following conditions:
• Excessively worn cylinder walls
• Worn piston or piston rings
• Piston rings stuck in grooves
• Poor valve seating
• Ruptured or otherwise defective cylinder head
gasket
Overhaul the engine in the following cases:
• Compression pressure in one of the cylinders is 1
000 kPa (10 kgf/cm
2
, 142 psi) and less.
• The difference in compression pressure between
any two cylinders is 200 kPa (2 kgf/cm
2
, 28 psi)
and more.
• All compression pressure readings are below 1
300 kPa (13 kgf/cm
2
, 185 psi) even when they
measure 1 000 kPa (10 kgf/cm
2
, 142 psi) and
more.
9) After checking the compression pressure, reinstall
the removed parts.
(A)
(B)
I718H1140380-01
Standard Limit Difference
1 300 – 1 700
kPa
(13 – 17 kgf/cm
2
,
185 – 242 psi)
1 000 kPa
(10 kgf/cm
2
, 142
psi)
200 kPa
(2 kgf/cm
2
, 28
psi)
I718H1140381-01

 Loading...
Loading...











