2: General operation Model DMM7510 7½ Digit Graphical Sampling Multimeter
2-140 DMM7510-901-01 Rev. B / May 2015
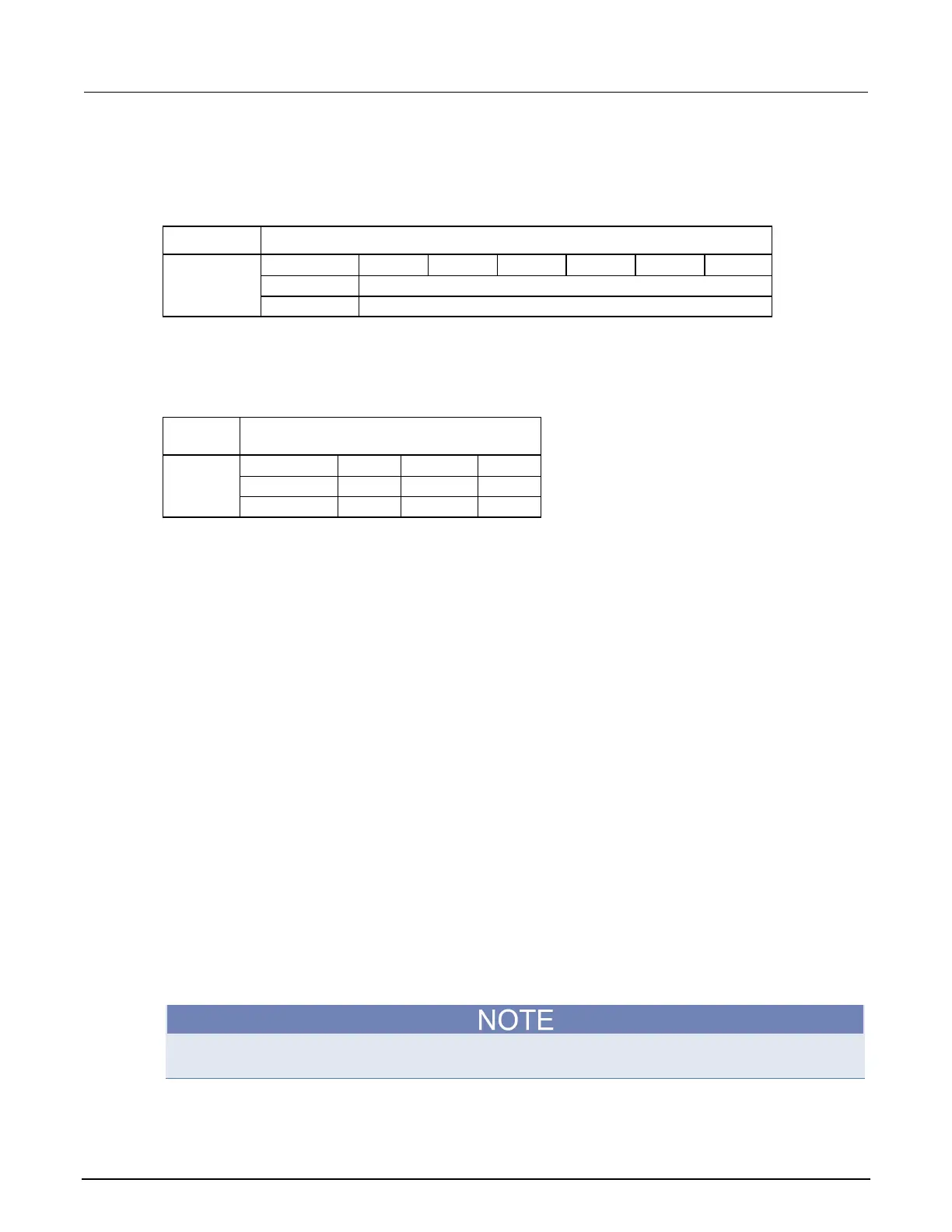
Capacitance autodelay and autorange times
The following table provides times for autodelay and autorange for the Model DMM7510 DMM
capacitance functions.
Function Range and delays
Capacitance
Range 1 nF 10 nF 100 nF
1 µF 100 µF
1 mF
Diode autodelay and autorange times
The following table provides times for autodelay and autorange for the Model DMM7510 DMM diode
functions.
Function Range and delays
Diode
µ
µ
DCV ratio autodelay and autorange times
The settle time for the DCV ratio function is the same as the settle time for the larger of the two
voltage ranges.
Detector bandwidth
You can select the detector bandwidth AC volt and AC current measurements. You can select 3 Hz,
30 Hz, or 300 Hz.
When you select the 3 Hz bandwidth, the signal goes through an analog root-mean-square (RMS)
converter. The output of the RMS converter goes to a fast (1 kHz) sampling A/D and the RMS value
is calculated from 1200 digitized samples (1.2 s).
When you select the 30 Hz bandwidth is chosen, the same converter is used. However, only 120
samples (120 ms) are needed for an accurate calculation because the analog RMS converter has
turned most of the signal to DC.
When you select the 300 Hz bandwidth, the output of the analog RMS converter (nearly pure DC at
these frequencies) is measured at an integration rate of 16.6 ms (1 power line cycle). You can set the
integration rate from 8.333 µs to 0.25 ms (60 Hz) and 10 µs to 0.24 ms (50 Hz).
To achieve the best accuracy for AC volt and AC current measurements, use the bandwidth setting
that best reflects the frequency of the input signal. For example, if the input signal is 40 Hz, a
bandwidth setting of 30 should be used.
You can only adjust the NPLC or aperture for AC voltage and AC current measurements when the
bandwidth for that function is set to 300 Hz.

 Loading...
Loading...