DTC 21, 28 Main Oxygen Sensor Circuit
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
ÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑ
Ñ
ÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑ
ÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑ
ÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑ
ÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑ
ÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑ
ÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑ
ÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑ
ÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑ
ÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑ
ÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑ
ÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑ
ÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑ
ÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑ
ÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑ
ÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑ
ÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑ
ÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑ
ÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑ
ÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑ
ÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑ
ÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑ
ÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑ
ÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑ
Ñ
ÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑ
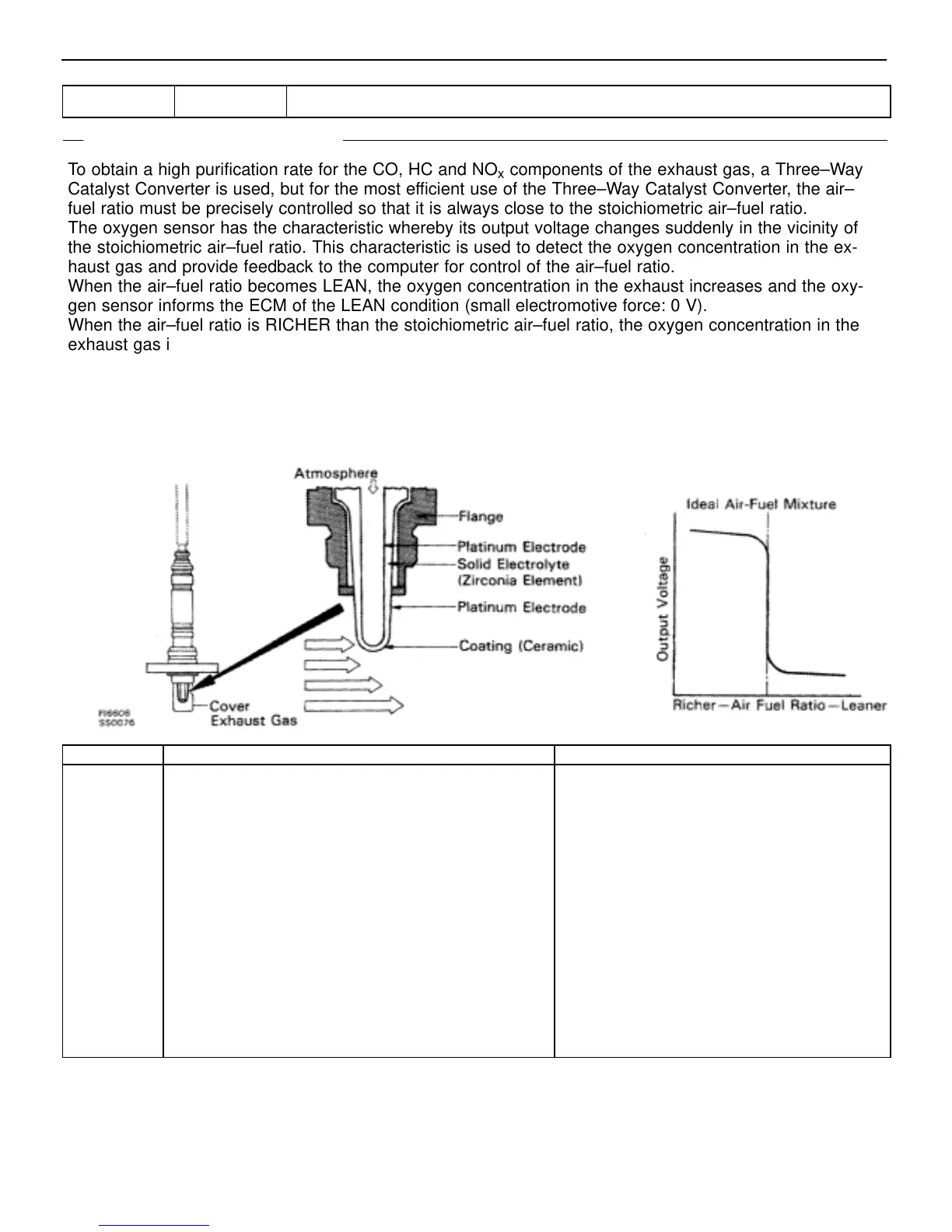
To obtain a high purification rate for the CO, HC and NO
x
components of the exhaust gas, a Three–Way
Catalyst Converter is used, but for the most efficient use of the Three–Way Catalyst Converter, the air–
fuel ratio must be precisely controlled so that it is always close to the stoichiometric air–fuel ratio.
The oxygen sensor has the characteristic whereby its output voltage changes suddenly in the vicinity of
the stoichiometric air–fuel ratio. This characteristic is used to detect the oxygen concentration in the ex-
haust gas and provide feedback to the computer for control of the air–fuel ratio.
When the air–fuel ratio becomes LEAN, the oxygen concentration in the exhaust increases and the oxy-
gen sensor informs the ECM of the LEAN condition (small electromotive force: 0 V).
When the air–fuel ratio is RICHER than the stoichiometric air–fuel ratio, the oxygen concentration in the
exhaust gas is reduced and the oxygen sensor informs the ECM of the RICH condition (large electromo-
tive force: 1 V).
The ECM judges by the electromotive force from the oxygen sensor whether the air–fuel ratio is RICH or
LEAN and controls the injection time accordingly. However, if malfunction of the oxygen sensor causes
output of abnormal electromotive force, the ECM is unable to perform accurate air–fuel ratio control.
Code No. Diagnostic Trouble Code Detecting Condition Trouble Area
21
28
Main oxygen sensor signal voltage is reduced to be-
tween 0.35 V and 0.70 V for 60 sec. under conditions
(a) (d).
(2 trip detection logic)*
(a) Engine coolant temp.: Between 70C (158F) and
90C (194F)
(b) Engine speed: 1,500 rpm or more
(c) Load driving (Ex. Electronic Controlled Transmis-
sion in 4th speed, A/C ON , flat road, 50 mph (80
km/h))
(d) Main oxygen sensor signal voltage:
Alternating above and below 0.45 V.
Main oxygen sensor circuit
Main oxygen sensor
*: See page EG–331.
HINT: Diag. trouble code 21 is for the left bank main oxygen sensor circuit. Diag. Trouble code 28 is for the right
bank main oxygen sensor circuit.
EG–366
–ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTING CIRCUIT INSPECTION

 Loading...
Loading...