Driver assistance systems
Using the ACC in the above situations may result in
accidents and serious injury,
and could commit legal infringements.
Limitations of the PCA
Please note at the beginning of this chapter on
page 140.
Do not use the ACC in the following cases
The ACC is not suitable for the following driving
situations due to system causes. Interrupt the
control → p. 140:
—
In case of heavy rain, snow or heavy water fog.
—
On roads with roadworks, tunnels or toll
stations.
—
On winding roads, e.g. on mountain roads.
—
On cross-country routes.
—
In covered car parks.
—
On tracks with integrated metal objects, e.g.
railway or tramway tracks.
—
On roads with loose gravel.
—
Vehicles without overtaking avoidance function
on the right: On multi-lane roads when other
vehicles are slowing down in the overtaking
lane.
Delayed reaction
When the radar sensor is exposed to environmental
conditions which impair its operation, the system
may detect this with a delay. Therefore, any
operating limitations at the start of the drive and
during the drive may be displayed with a delay.
→ p. 140.
Undetected objects
The radar sensor only detects vehicles moving in the
same direction. It does not detect:
—
Persons
—
Animals
—
Vehicles detained
—
Vehicles travelling in the opposite direction or
passing each other
—
Other immovable obstacles
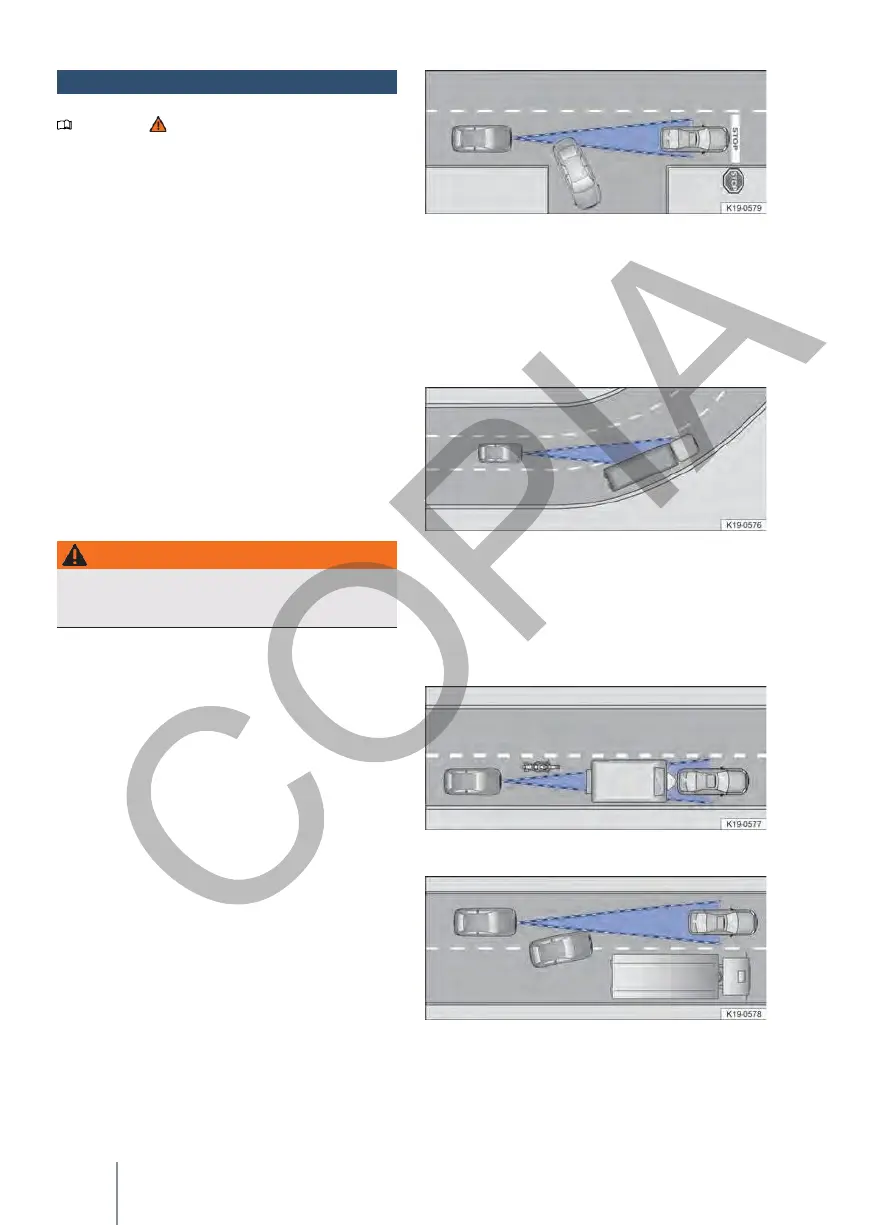
Fig. 119 Vehicle turning and another stopped.
If, for example, a vehicle detected by the ACC
turns or moves away and a stationary vehicle is in
front of it, the ACC does not react to the stationary
vehicle.
mo → fig. 119.
Curves
Fig. 120 Curved section.
The radar sensor always measures in a straight
line. Therefore, on sharp bends it may detect
vehicles incorrectly or may not detect vehicles
ahead → Fig. 120.
Vehicles outside the sensor zone
Fig. 121 Narrow vehicle.
Fig. 122 Lane change.

 Loading...
Loading...











