WHEEL ALIGNMENT
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
WHEEL ALIGNMENT
DESCRIPTION .........................17
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRE-ALIGNMENT
INSPECTION .........................17
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TOE
ADJUSTMENT ........................19
SPECIFICATIONS .......................19
WHEEL ALIGNMENT
DESCRIPTION
NOTE: Camber and Caster are not adjustable on
this vehicle. (TOE ONLY).
NOTE: Suspension components with rubber/ure-
thane bushings should be tightened with the vehi-
cle at normal ride height. It is important to have the
springs supporting the weight of the vehicle when
the fasteners are torqued. If springs are not at their
normal ride position, vehicle ride comfort could be
affected and premature bushing wear may occur.
Wheel alignment involves the correct positioning of
the wheels in relation to the vehicle. The positioning
is accomplished through suspension and steering
linkage adjustments. An alignment is considered
essential for efficient steering, good directional stabil-
ity and to minimize tire wear. The most important
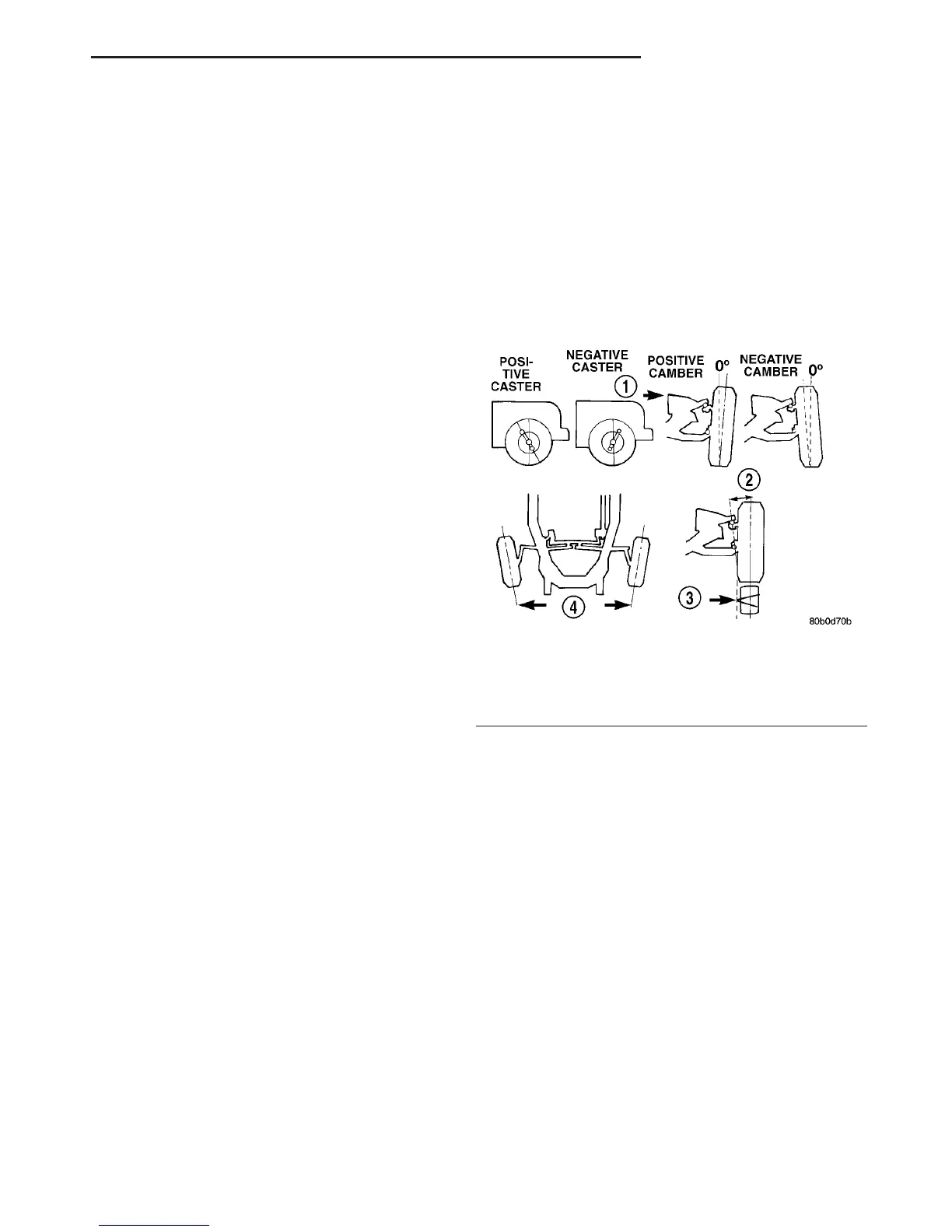
measurements of an alignment are caster, camber
and toe (Fig. 1).
CAUTION: Never attempt to modify suspension or
steering components by heating or bending.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRE-ALIGNMENT
INSPECTION
Before starting wheel alignment, the following
inspection and necessary corrections must be com-
pleted. Refer to Suspension and Steering System
Diagnosis Chart below for additional information.
(1) Inspect tires for size, air pressure and tread
wear.
(2) Inspect front wheel bearings for wear.
(3) Inspect front wheels for excessive radial or lat-
eral runout and balance.
(4) Inspect ball studs, linkage pivot points and
steering gear for looseness, roughness or binding.
(5) Inspect suspension components for wear and
noise.
(6) Road test the vehicle.
Fig. 1 Wheel Alignment Measurements
1 - FRONT OF VEHICLE
2 - STEERING AXIS INCLINATION
3 - PIVOT POINT
4 - TOE-IN
VA WHEEL ALIGNMENT 2 - 17

 Loading...
Loading...











