SHIFT GROUPS
The hydraulic control components (including actua-
tors) which are responsible for the pressure distribu-
tion before, during, and after a gear change are
described as a shift group. Each shift group contains
a command valve, a holding pressure shift valve, a
shift pressure shift valve, overlap regulating valve,
and a solenoid.
The hydraulic system contains three shift groups:
1-2/4-5, 2-3, and 3-4. Each shift group can also be
described as being in one of two possible states. The
active shift group is described as being in the shift
phase when it is actively engaging/disengaging a
clutch combination. The 1-2/4-5 shift group control
the B1 and K1 clutches. The 2-3 shift group controls
the K2 and K3 clutches. The 3-4 shift group controls
the K3 and B2 clutches.
OPERATION
The transmission control is divided into the elec-
tronic and hydraulic transmission control functions.
While the electronic transmission control is responsi-
ble for gear selection and for matching the pressures
to the torque to be transmitted, the transmission’s
power supply control occurs via hydraulic elements
in the electrohydraulic control module. The oil supply
to the hydraulic elements, such as the hydrodynamic
torque converter, the shift elements and the hydrau-
lic transmission control, is provided by way of an oil
pump connected with the torque converter.
The Transmission Control Module (TCM) allows for
the precise adaptation of pressures to the correspond-
ing operating conditions and to the engine output
during the gearshift phase, resulting in a noticeable
improvement in shift quality. The engine speed limit
can be reached in the individual gears at full throttle
and kickdown. The shift range can be changed in the
forward gears while driving, but the TCM employs a
downshift safeguard to prevent over-revving the
engine. The system offers the additional advantage of
flexible adaptation to different vehicle and engine
variants.
EMERGENCY RUNNING FUNCTION
In order to ensure a safe driving state and to pre-
vent damage to the automatic transmission, the TCM
control module switches to limp-home mode in the
event of critical faults. A DTC assigned to the fault is
stored in memory. All solenoid and regulating valves
are thus de-energized.
The net effect is:
• The last engaged gear remains engaged.
• The modulating pressure and shift pressures
rise to the maximum levels.
• The torque converter lockup clutch is deacti-
vated.
In order to preserve the operability of the vehicle
to some extent, the hydraulic control can be used to
engage 2nd gear or reverse using the following pro-
cedure:
• Stop the vehicle.
• Switch off engine.
• Move selector lever to 9P9.
• Wait at least 10 seconds.
• Start engine.
• Move selector lever to D: 2nd gear.
• Move selector lever to R: Reverse gear.
The limp-home function remains active until the
DTC is rectified or the stored DTC is erased with the
DRBt tool. Sporadic faults can be reset via ignition
OFF/ON.
CLUTCH APPLICATION
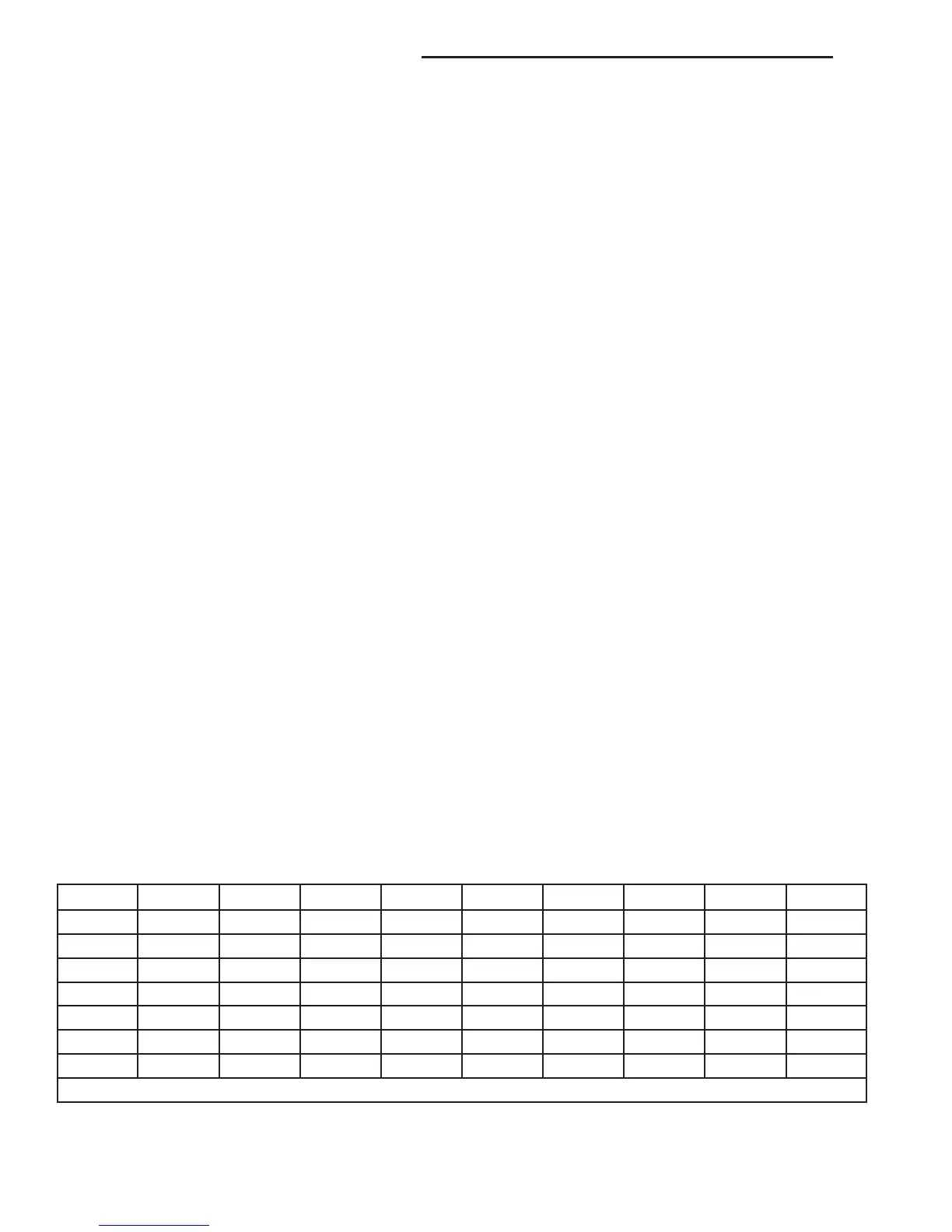
Refer to CLUTCH APPLICATION for which shift
elements are applied in each gear position.
CLUTCH APPLICATION
GEAR RATIO B1 B2 B3 K1 K2 K3 F1 F2
1 3.59 X* X X* X X
2 2.19 X X X* X
3 1.41 X X X
4 1.00 X X X
5 0.83 X X X X*
NX X
R 3.16 X* X X X
* = The shift components required during coast.
21 - 4 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - NAG1 VA
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - NAG1 (Continued)

 Loading...
Loading...











