Lenze · 8400 HighLine · Reference manual · DMS 12.0 EN · 06/2017 · TD23 733
11 System bus "CAN on board"
11.8 Process data transfer
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
11.8.4 Synchronisation of PDOs via sync telegram
During cyclic transmission, one or more PDOs are transmitted/received in fixed time intervals. An
additional specific telegram, the so-called sync telegram, is used for synchronising cyclic process
data.
• The sync telegram is the trigger point for the transmission of process data from the slaves to the
master and for the acceptance of process data from the master in the slaves.
• For sync-controlled process data processing, the sync telegram must be generated accordingly.
• The response to a sync telegram is determined by the transmission type selected.
Transmission type
( 731)
Basic workflow
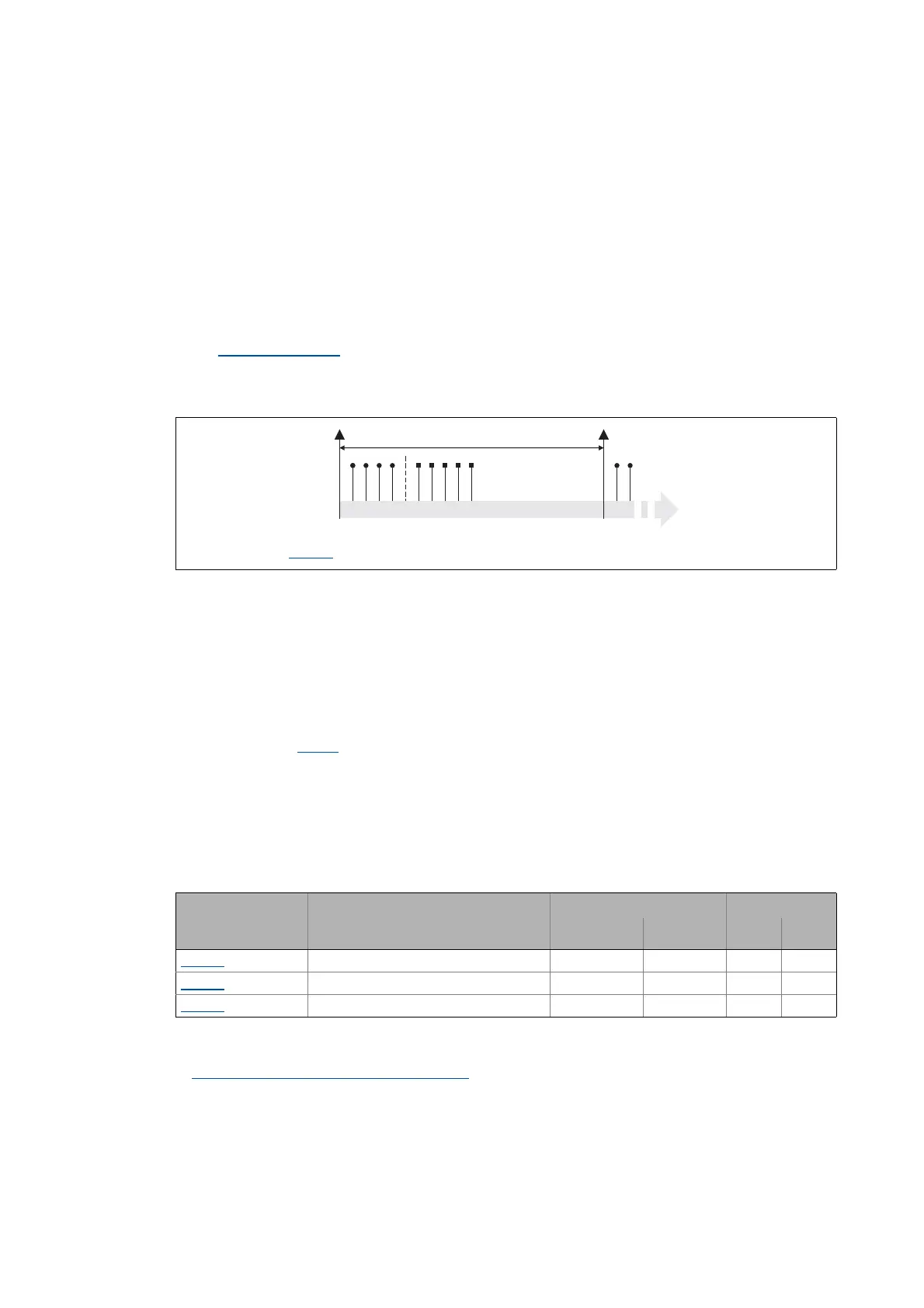
[11-6] Sync telegram
A. After the sync telegram has been received, the slaves transmit the synchronous process data to
the master (TPDOs). The master reads them as process input data.
B. When the transmission process is completed, the slaves receive (RPDOs) the process output
data (of the master).
• All other telegrams (e.g. parameters or event-controlled process data) are accepted acyclically
by the slaves after the transmission is completed.
• Illustration [11-6]
does not include acyclic data. However, they need to be considered when
dimensioning the cycle time.
C. The data are accepted in the slave with the next sync telegram if the Rx mode is set to 1 ... 240.
If the Rx mode is 254 or 255, the data are accepted in the next device cycle, irrespective of the
sync telegram.
Short overview: Parameters for the synchronisation via sync telegram
Related topics:
Synchronisation of the internal time base
( 787)
Sync cycle time (C01121)
Parameters Info Lenze setting Assignment
Value Unit Sync
master
Sync
slave
C00367 CAN SYNC Rx identifier 0x0080
C00368
CAN SYNC Tx identifier 0x0080
C00369
CAN sync transmission cycle time 0 ms

 Loading...
Loading...















