Configuring and Viewing Device Port Information
D-Link Unified Wired and Wireless Access System
Oct. 2015 Page 110
D-Link UWS User Manual
Port Summary
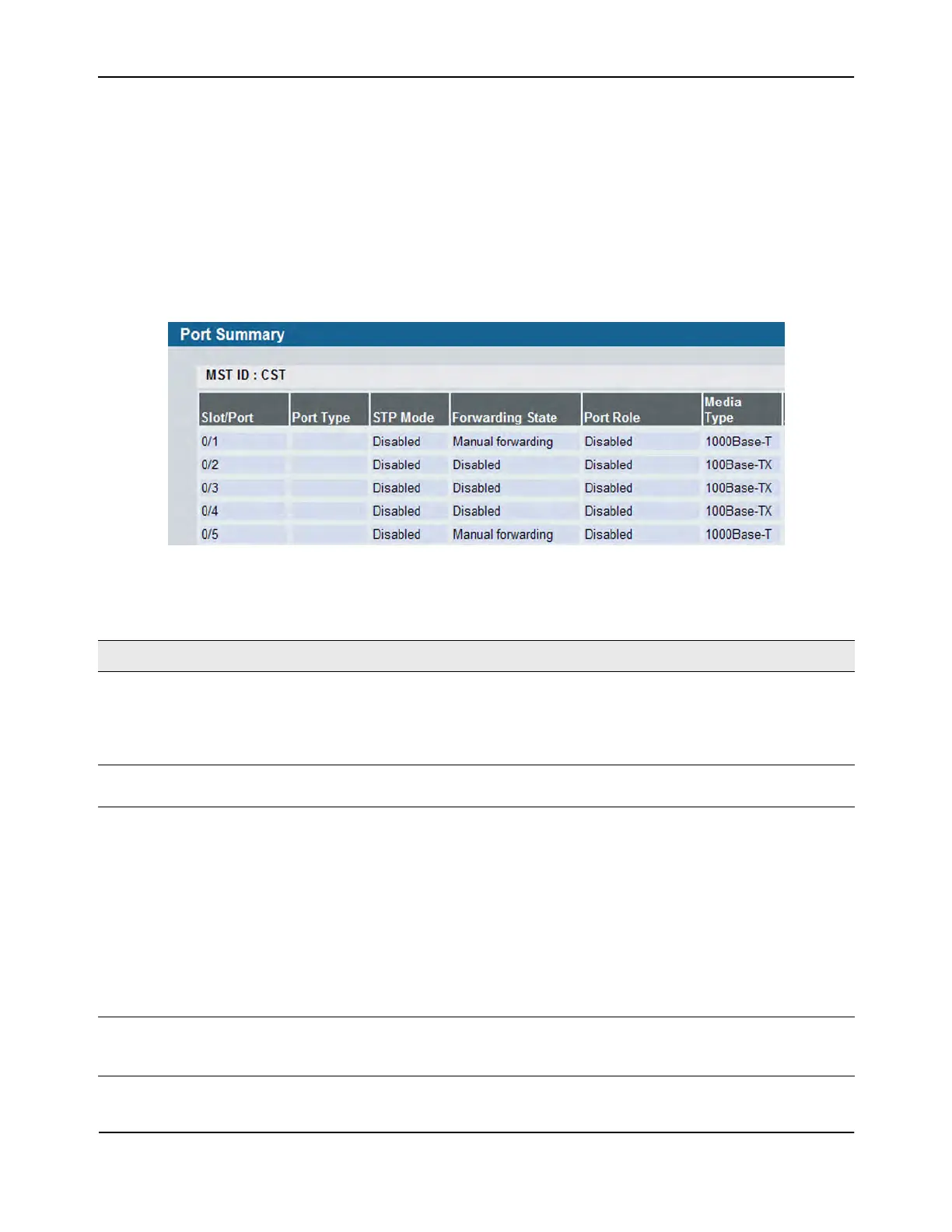
Use the Port Summary page to view the settings for all physical ports on the platform.
To access the Port Summary page, click LAN > Monitoring > Port Utilization in the navigation menu.
The table on the Port Summary page does not fit on one screen. Use the scroll bar at the bottom of the
browser to view all the columns on the page. Figure 39 shows the first six rows of all the columns on the page.
Although the table is split into three separate images in the figure, the columns are continue horizontally
across the page.
Figure 39: Port Summary
Table 34: Port Summary Fields
Field Description
MST ID If Spanning Tree Protocol is enabled on the switch, you can select the Multiple
Spanning Tree instance ID from the list of all currently configured MST ID's to
determine the values displayed for the Spanning Tree parameters. Changing
the selected MST ID will generate a screen refresh. If is disabled, which is the
default, the MST ID field shows the static value “CST” instead of a menu.
Slot/Port Identifies the port that the information in the rest of the row is associated
with.
Port Type For most ports this field is blank. Otherwise, the possible values are:
• Mirrored: Indicates that the port has been configured as a monitoring port
and is the source port in a port mirroring session.
• Probe: Indicates that the port has been configured as a monitoring port
and is the destination port in a port mirroring session. For more
information about port monitoring and probe ports, see “Multiple Port
Mirroring” on page 90.
• Port Channel: Indicates that the port has been configured as a member of
a port-channel, which is also known as a link Aggregation Group (LAG). For
information about configuring port channels, see “Creating Port Channels
(Trunking)” on page 209.
Mode Shows the Spanning Tree Protocol () Administrative Mode for the port or LAG,
which can be Enabled or Disabled. For more information about , see
“Configuring Spanning Tree Protocol” on page 243.

 Loading...
Loading...











