Managing and Viewing Logs
D-Link Unified Wired and Wireless Access System
Oct. 2015 Page 120
D-Link UWS User Manual
Deleting a Remote Logging Host
To delete a remote logging host from the configured list, select the IP address of the host from the Host field,
and then click Delete.
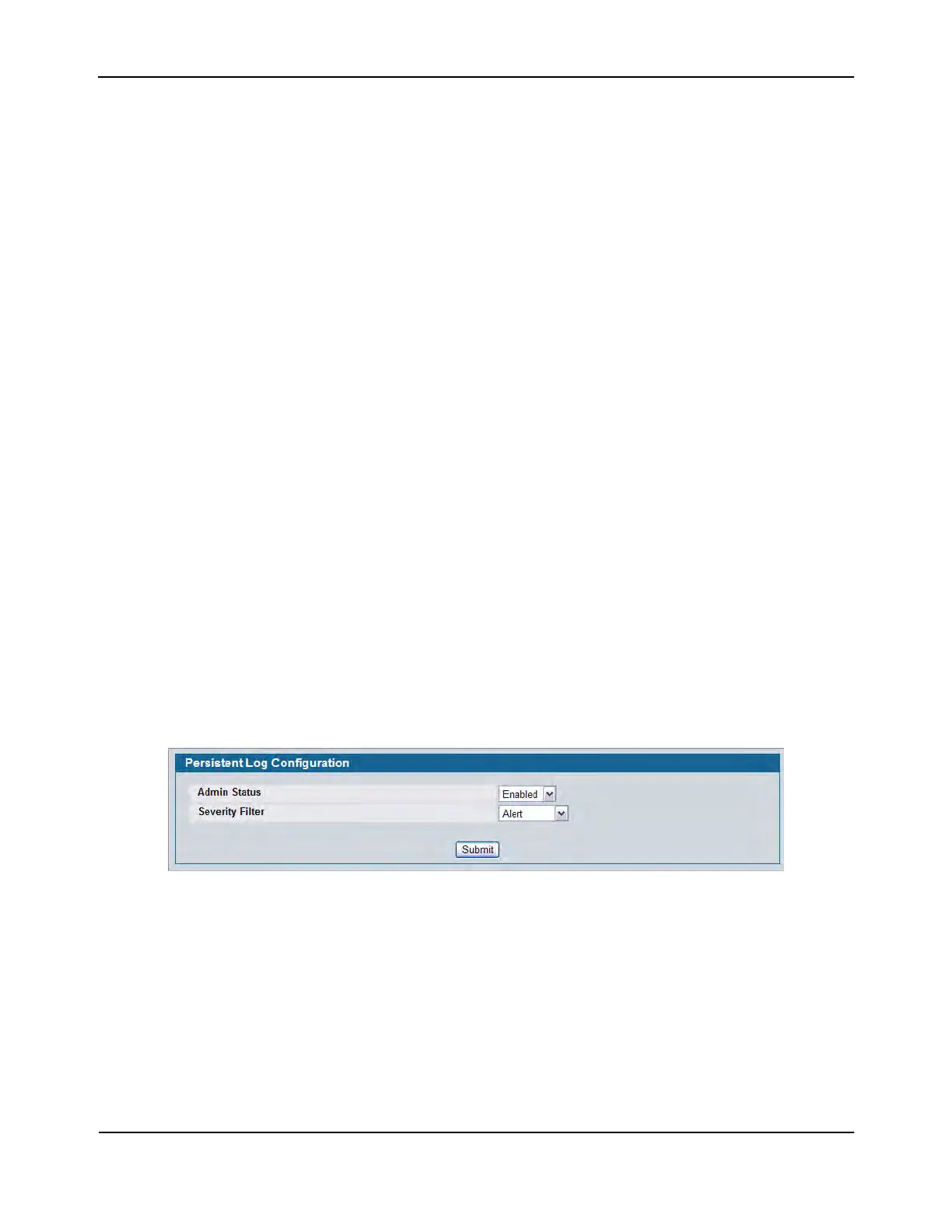
Persistent Log Configuration
The persistent log is stored in persistent storage, which means that the log messages are retained across a
switch reboot.
• The first log type is the system startup log. The system startup log stores the first N messages received
after system reboot. This log always has the log full operation attribute set to stop on full and can store up
to 32 messages.
• The second log type is the system operation log. The system operation log stores the last N messages
received during system operation. This log always has the log full operation attribute set to overwrite.
This log can store up to 1000 messages.
Either the system startup log or the system operation log stores a message received by the log subsystem that
meets the storage criteria, but not both. In other words, on system startup, if the startup log is configured, it
stores messages up to its limit. The operation log, if configured, then begins to store the messages.
The system keeps up to three versions of the persistent logs, named <FILE>1.txt, <FILE>2.txt, and <FILE>3.txt.
Upon system startup, <FILE>3.txt is removed, <FILE>2.txt is renamed <FILE>3.txt, <FILE>1.txt is renamed
<FILE>2.txt, <FILE>1.txt is created and logging begins into <FILE>1.txt. (Replace <FILE> in the above example
to specify
olog for the operation log and slog for the startup log.)
The local persistent logs can be retrieved via the Web or CLI, or via xmodem over the local serial cable.
Use the Persistent Log Configuration page to enable or disable persistent logging and to set the severity filter.
To access the Persistent Log Configuration page, click LAN > Administration > Log > Persistent Logger
Configuration in the navigation menu.
Figure 48: Persistent Log Configuration

 Loading...
Loading...











